Basic Electron Configuration Pdf Electron Configuration Energy Level

Basic Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Energy Level
Basic Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Energy Level To write out the electron configuration you need to determine the number of electrons using the periodic table and fill up each orbital in order, starting with 1s, until you run out of electrons. Transition metals do not always exhibit regular patterns in their electron configurations but have some similarities as a whole such as colored compounds and multiple oxidation states.

Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Atomic Orbital
Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Atomic Orbital Electron configuration and the periodic table the electrons in an atom fill from the lowest to the highest orbitals. the knowledge of the location of the orbitals on the periodic table can greatly help the writing of electron configurations for large atoms. Electrons are found to have a property called spin. spin can be thought of as rotation relative to a magnetic pole. ‣ spin can be demonstrated by applying a magnetic fields, which increases electron splitting. there are only two kinds of spin, spin up (↑) and spin down (↓). Aufbau diagram (above right) shows relative energies of different orbitals in many electron atoms. sublevels split in multi electron atoms due to shielding (we’ll discuss this next class). The electrons in an atom exist in various energy levels. when an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, energy is absorbed by the atom.

Lect-4 Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Ion
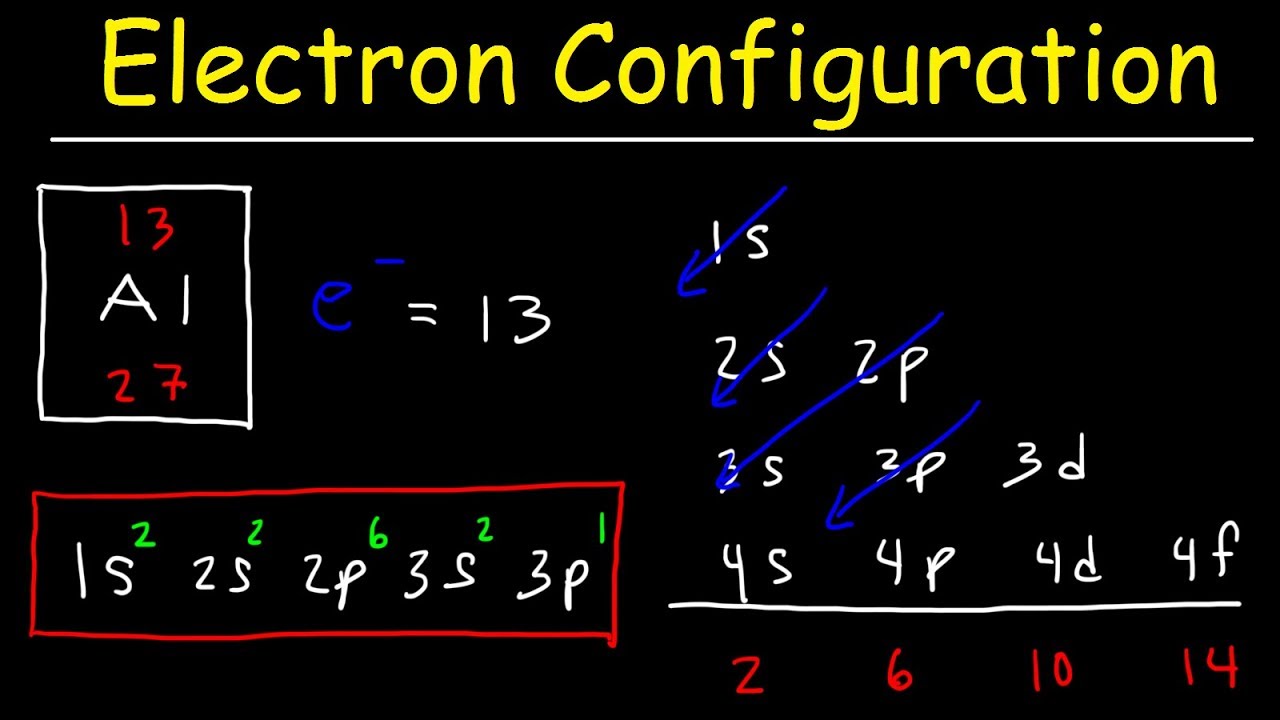
Lect-4 Electron Configuration | PDF | Electron Configuration | Ion Aufbau diagram (above right) shows relative energies of different orbitals in many electron atoms. sublevels split in multi electron atoms due to shielding (we’ll discuss this next class). The electrons in an atom exist in various energy levels. when an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, energy is absorbed by the atom. Electron configuration is a method of indicating the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus. a typical e. ectron configuration consists of numbers, letters, and superscripts with the following format: a number indicates the energy l. el (the number is called the principal quantum numb. The electrons in the outermost energy level are called valence electrons. the first four elements have a stable state with only the first energy level consisting of two 1s electrons. all other elements have a stable configuration that includes both s and p orbitals. To predict the electron configuration for an atom’s ground state, the lowest energy state for an atom, electrons are put into the orbitals with the lowest energy possible, placing no more than two electrons in an orbital. Fill orbitals across energy levels: starting from the lowest energy orbital, move across periods (rows) on the periodic table to fill orbitals (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, etc.). verify electron count: the total number of electrons used should match the atomic number of the element.

Electron Configurations Lesson | PDF | Electron Configuration | Atomic Orbital
Electron Configurations Lesson | PDF | Electron Configuration | Atomic Orbital Electron configuration is a method of indicating the arrangement of electrons about a nucleus. a typical e. ectron configuration consists of numbers, letters, and superscripts with the following format: a number indicates the energy l. el (the number is called the principal quantum numb. The electrons in the outermost energy level are called valence electrons. the first four elements have a stable state with only the first energy level consisting of two 1s electrons. all other elements have a stable configuration that includes both s and p orbitals. To predict the electron configuration for an atom’s ground state, the lowest energy state for an atom, electrons are put into the orbitals with the lowest energy possible, placing no more than two electrons in an orbital. Fill orbitals across energy levels: starting from the lowest energy orbital, move across periods (rows) on the periodic table to fill orbitals (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, etc.). verify electron count: the total number of electrons used should match the atomic number of the element.

Electron Configurations Worksheet
Electron Configurations Worksheet To predict the electron configuration for an atom’s ground state, the lowest energy state for an atom, electrons are put into the orbitals with the lowest energy possible, placing no more than two electrons in an orbital. Fill orbitals across energy levels: starting from the lowest energy orbital, move across periods (rows) on the periodic table to fill orbitals (1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, etc.). verify electron count: the total number of electrons used should match the atomic number of the element.
Electron Configuration - Basic introduction
Electron Configuration - Basic introduction
Related image with basic electron configuration pdf electron configuration energy level
Related image with basic electron configuration pdf electron configuration energy level
About "Basic Electron Configuration Pdf Electron Configuration Energy Level"
















Comments are closed.