Capacitation Acrosome Reaction Fertilisation

Chapter 47 Animal Development. - Ppt Download
Chapter 47 Animal Development. - Ppt Download During mammalian fertilization, the capacitated spermatozoon penetrates the cumulus oophrous of the ovum, and then binds to the zona pellucida (zp) with its plasma membrane intact. Other spermatozoa become prematurely capacitated and destined for death, with only a few dozen spermatozoa reaching the site of fertilization in the oviductal isthmus.

PPT - The Female Reproductive System PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID:1281711
PPT - The Female Reproductive System PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID:1281711 Sperm undergo the acrosome reaction before fertilization in order to penetrate the zona pellucida (zp) of the oocyte. this process occurs following binding to the zp only if the sperm have previously undergone a maturation process called capacitation. We will highlight recent advances which suggest that capacitation and induction of the acrosome reaction are regulated by multiple interactions between ca 2 , sperm pm enzymes and lipids. The acrosome reaction (ar) is an essential process of spermatozoa for fertilization and is characterized by the exocytosis of the acrosomal content and the release of hybrid membrane vesicles formed by patches of the outer acrosomal membrane and the plasma membrane. To achieve successful fertilization under normal circumstances in vivo, mammalian spermatozoa must first undergo capacitation and then the acrosome reaction, an exocytotic event that allows cells to penetrate the zona pellucida and fuse with the oocyte plasma membrane.

EARLY EMBRYOGENESIS Article With Diagrams | PPT
EARLY EMBRYOGENESIS Article With Diagrams | PPT The acrosome reaction (ar) is an essential process of spermatozoa for fertilization and is characterized by the exocytosis of the acrosomal content and the release of hybrid membrane vesicles formed by patches of the outer acrosomal membrane and the plasma membrane. To achieve successful fertilization under normal circumstances in vivo, mammalian spermatozoa must first undergo capacitation and then the acrosome reaction, an exocytotic event that allows cells to penetrate the zona pellucida and fuse with the oocyte plasma membrane. As part of capacitation, sperm develop an asymmetrical flagellar beating known as hyperactivation and acquire the ability to undergo the acrosome reaction. together, these processes promote fertilizing competence in sperm. To acquire the capacity to fertilize the oocyte, mammalian spermatozoa must undergo a series of biochemical reactions in the female reproductive tract, which are collectively called capacitation. Peter sutovsky abstract recent advances in our understanding of fertilization are summarized, highlighting newly discov ered molecules implicated in sperm interactions with the epithelia of the female reproductive system (spermadhesins, bsp proteins), sperm–zona binding (zp4, zp3r, iam38/ zpbp), sperm oolemma binding and fusion (izumo, cd9, cd81), oocyte activation (plczeta, src family. In this article, we have reviewed the data from our and other laboratories, and have constructed a heuristic model for the mechanisms and molecules involved in capacitation/acrosome reaction. the process of fertilization is characterized by a series of complex set of events.
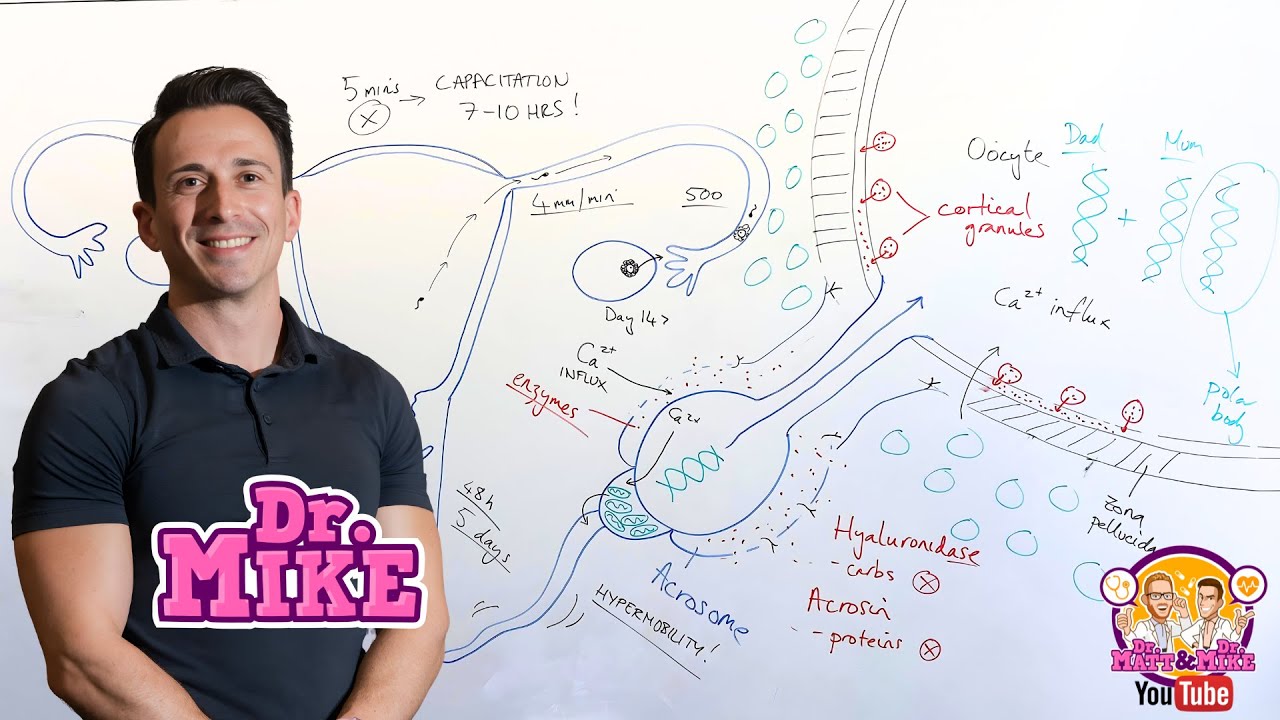
Capacitation & Acrosome Reaction | Fertilisation
Capacitation & Acrosome Reaction | Fertilisation
Related image with capacitation acrosome reaction fertilisation
Related image with capacitation acrosome reaction fertilisation
About "Capacitation Acrosome Reaction Fertilisation"
















Comments are closed.