Define Bond Order How Are Bond Energy And Bond Length Related To Bond Order Why Are There

Define Bond Order. How Are Bond Energy And Bond Length Related To Bond Order? Why Are There ...
Define Bond Order. How Are Bond Energy And Bond Length Related To Bond Order? Why Are There ... Bond order is the number of electron pairs that hold two atoms together. single bonds have a bond order of one, and multiple bonds with bond orders of two (a double bond) and three (a triple bond) …. It represents the equilibrium distance where the attractive and repulsive forces between the atoms are balanced. bond length is influenced primarily by the bond order, which is the number of shared electron pairs between two atoms. it is typically measured in picometers (pm) or angstroms (Å).

Solved QUESTION 6 In General How Are Bond Order, Bond Length | Chegg.com
Solved QUESTION 6 In General How Are Bond Order, Bond Length | Chegg.com Single bonds have a bond order of 1, double bonds have a bond order of 2, and triple bonds have a bond order of 3. higher bond orders correspond to stronger bonds. stronger bonds have shorter bond lengths and higher bond energies. bond order directly impacts bond strength and stability. Bond order refers to the number of chemical bonds formed between two atoms in a molecule. for example, two atoms of hydrogen combine to form a hydrogen molecule (h h or h 2). therefore, the bond order of h 2 is one. similarly, the bond order of oxygen (o=o or o 2) is two and that of nitrogen (n ≡ n or n 2) is three. Several bond parameters, such as bond length, bond angle, bond order, and bond energy, can be used to characterize covalent bonds (also known as bond enthalpy). these bond parameters provide information about the stability of a chemical compound as well as the strength of the chemical bonds that hold its atoms together. what is a bond?. Define the term average bond enthalpy. explain the concept of bond energy. exothermic and others are endothermic. calculate the heats of reaction for bond energies. bonds between atoms. bond order and length are inversely proportional to. each other. when bond order is increased, bond length is decreased. atoms.

SOLVED:Define Bond Length And Bond Energy.
SOLVED:Define Bond Length And Bond Energy. Several bond parameters, such as bond length, bond angle, bond order, and bond energy, can be used to characterize covalent bonds (also known as bond enthalpy). these bond parameters provide information about the stability of a chemical compound as well as the strength of the chemical bonds that hold its atoms together. what is a bond?. Define the term average bond enthalpy. explain the concept of bond energy. exothermic and others are endothermic. calculate the heats of reaction for bond energies. bonds between atoms. bond order and length are inversely proportional to. each other. when bond order is increased, bond length is decreased. atoms. Bond order help us to understand the relationship between bond length, bond energy, bond strength (shriver, atkins, langford 1990). the bond energy increase with bond order and the length decreases as the bond order increases. This means that the more the number of bonds, the stronger it is to break. hence, triple bonds are stronger than double bonds, and double bonds are stronger than single bonds. Coulomb's law states that the bond energy is inversely related to the bond length (r), and so factors which influence a bond's strength influence its length. this can allow us to determine some trends in bond lengths. Bond parameters are basic properties that describe covalent bonds between atoms. they include: bond order: the number of pairs of electrons shared between two atoms. the concept is quantifiable from a lewis structure of a molecule and describes the strength and therefore stability of a bond.

Bond Order Vs. Bond Length | ChemTalk
Bond Order Vs. Bond Length | ChemTalk Bond order help us to understand the relationship between bond length, bond energy, bond strength (shriver, atkins, langford 1990). the bond energy increase with bond order and the length decreases as the bond order increases. This means that the more the number of bonds, the stronger it is to break. hence, triple bonds are stronger than double bonds, and double bonds are stronger than single bonds. Coulomb's law states that the bond energy is inversely related to the bond length (r), and so factors which influence a bond's strength influence its length. this can allow us to determine some trends in bond lengths. Bond parameters are basic properties that describe covalent bonds between atoms. they include: bond order: the number of pairs of electrons shared between two atoms. the concept is quantifiable from a lewis structure of a molecule and describes the strength and therefore stability of a bond.
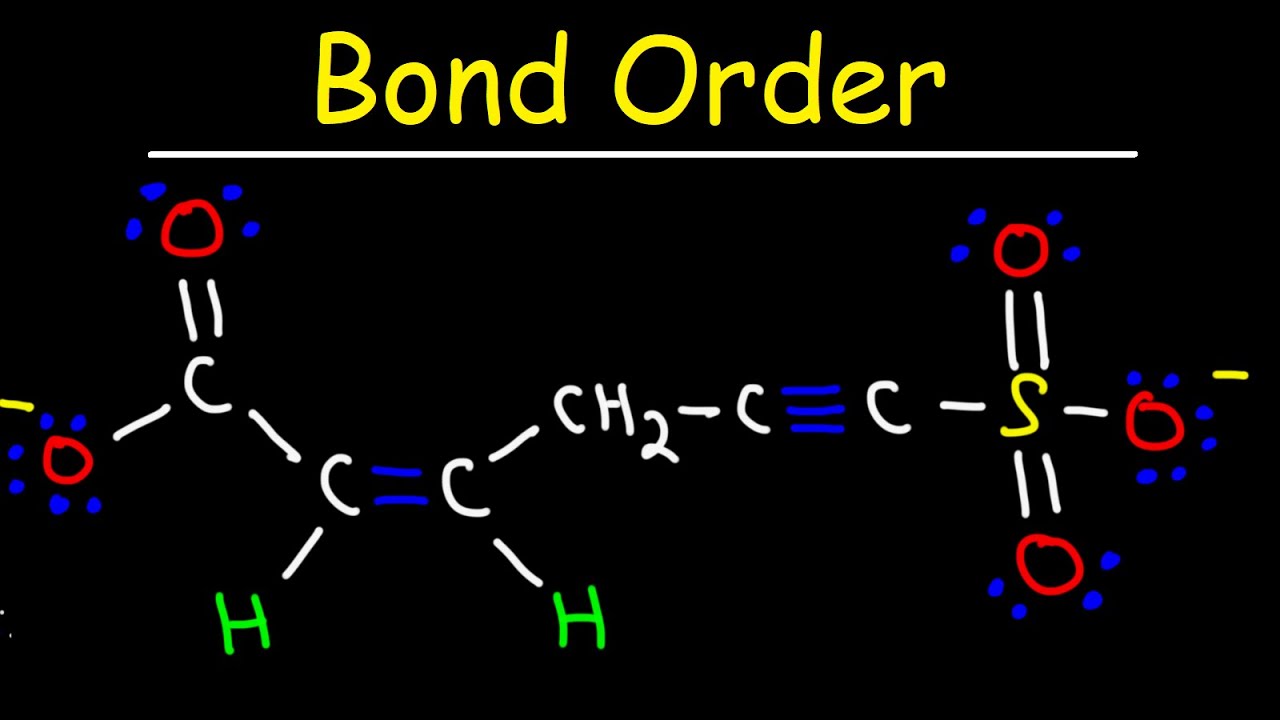
Bond Order and Resonance Structures
Bond Order and Resonance Structures
Related image with define bond order how are bond energy and bond length related to bond order why are there
Related image with define bond order how are bond energy and bond length related to bond order why are there
About "Define Bond Order How Are Bond Energy And Bond Length Related To Bond Order Why Are There"












Comments are closed.