Electricity And Magnetism2 Pdf Ion Electromagnetic Induction

Electromagnetic Induction | PDF
Electromagnetic Induction | PDF Electromagnetic induction encompasses two phenomena. the first involves a current that is induced in a conductor moving relative to magnetic field lines. the second involves the generation of an electric field associated with a time dependent magnetic field. For 50 years, edward m. purcell’s classic textbook has introduced students to the world of electricity and magnetism. this third edition has been brought up to date and is now in si units. it features hundreds of new examples, problems, and figures, and contains discussions of real life applications.

Electromagnetic Induction | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Magnetic Field
Electromagnetic Induction | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Magnetic Field Download, borrow, or stream the cengage magnetism content for free from this online archive. In electromagnetism, faraday's law of induction describes how a changing magnetic field can induce an electric current in a circuit. this phenomenon, known as electromagnetic induction, is the fundamental operating principle of transformers, inductors, and many types of electric motors, generators and solenoids. [1][2] "faraday's law" is used in the literature to refer to two closely related. When a magnetic field changes over time, this can induce an electric potential difference called an induced emf, this causes charge to flow in a closed loop of wire which is called an induced current. Lesson 2 covers magnetism and electromagnetic induction, explaining that magnetic fields arise from magnets and moving electric charges. it details the relationship between electricity and magnetism, including ampere's law and faraday's law, which describe how magnetic fields can induce electric currents.

Electromagnetic Induction | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Inductance
Electromagnetic Induction | PDF | Electromagnetic Induction | Inductance When a magnetic field changes over time, this can induce an electric potential difference called an induced emf, this causes charge to flow in a closed loop of wire which is called an induced current. Lesson 2 covers magnetism and electromagnetic induction, explaining that magnetic fields arise from magnets and moving electric charges. it details the relationship between electricity and magnetism, including ampere's law and faraday's law, which describe how magnetic fields can induce electric currents. While the magnetic flux through a circuit is changing, an emf is generated in the circuit which is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux \ (\dot \phi b\) through the circuit. this is generally called " faraday's law of electromagnetic induction". In this chapter, we will study the phenomena associated with changing magnetic fields and understand the underlying principles. the phenomenon in which electric current is generated by varying magnetic fields is appropriately called electromagnetic induction. Transforms low voltage to high voltage. if the induced current reinforced the change then the change would get bigger which would then induce a larger current and then the change would get even bigger and so on . . . a clear violation of conservation of energy!!. G. brown 1993, 2007, 2013 notice this physics textbook is designed to support my personal teaching activities at duke university, in particular teaching its physics 141/142, 151/152, or 161/162 series (introduc tory physics for life science majors, engineers, or potent.

Electromagnetic Induction | PDF
Electromagnetic Induction | PDF While the magnetic flux through a circuit is changing, an emf is generated in the circuit which is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux \ (\dot \phi b\) through the circuit. this is generally called " faraday's law of electromagnetic induction". In this chapter, we will study the phenomena associated with changing magnetic fields and understand the underlying principles. the phenomenon in which electric current is generated by varying magnetic fields is appropriately called electromagnetic induction. Transforms low voltage to high voltage. if the induced current reinforced the change then the change would get bigger which would then induce a larger current and then the change would get even bigger and so on . . . a clear violation of conservation of energy!!. G. brown 1993, 2007, 2013 notice this physics textbook is designed to support my personal teaching activities at duke university, in particular teaching its physics 141/142, 151/152, or 161/162 series (introduc tory physics for life science majors, engineers, or potent.

Electromagnetic Induction | PDF
Electromagnetic Induction | PDF Transforms low voltage to high voltage. if the induced current reinforced the change then the change would get bigger which would then induce a larger current and then the change would get even bigger and so on . . . a clear violation of conservation of energy!!. G. brown 1993, 2007, 2013 notice this physics textbook is designed to support my personal teaching activities at duke university, in particular teaching its physics 141/142, 151/152, or 161/162 series (introduc tory physics for life science majors, engineers, or potent.
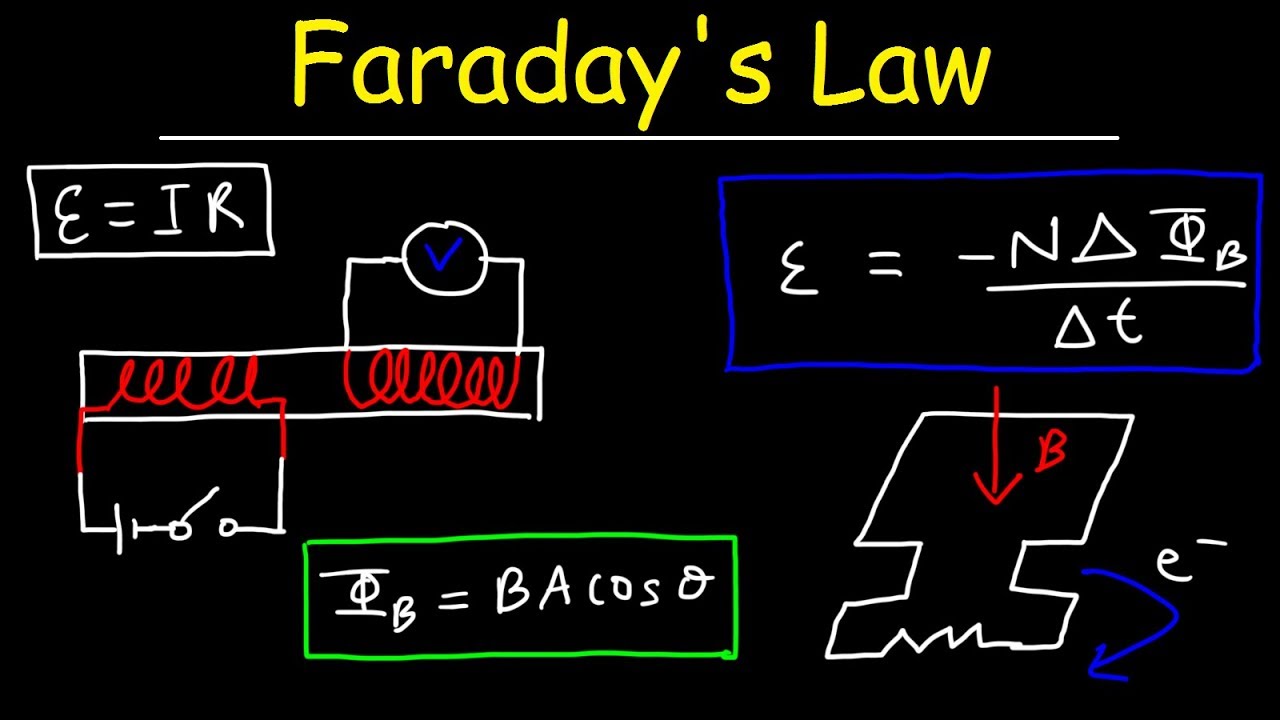
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction, Magnetic Flux & Induced EMF - Physics & Electromagnetism
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction, Magnetic Flux & Induced EMF - Physics & Electromagnetism
Related image with electricity and magnetism2 pdf ion electromagnetic induction
Related image with electricity and magnetism2 pdf ion electromagnetic induction
About "Electricity And Magnetism2 Pdf Ion Electromagnetic Induction"
















Comments are closed.