Electrostatics Electric Charges Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes

Electrostatics Electric Charges Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes – Artofit
Electrostatics Electric Charges Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes – Artofit The discussion clarifies the relationship between the electric displacement field (d) and the electric field (e) in the context of electrostatics, particularly within isotropic, linear, and homogeneous dielectrics. it emphasizes that the divergence of d relates to free charge density (rho), while the divergence of e involves both free and bound charges. the participants correct a. In three dimensions, electrostatic fields can be modeled using poisson's equation, resulting in a potential function that decays as 1/ (4 pi r) and an electric field that follows the inverse square law. in contrast, two dimensional electrostatics yield a potential function of u = 1/ (2 pi log (r)), leading to a field that decays as 1/r, rather than 1/r². this difference arises because, in two.

Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Electric Charges And Fields | Toppers CBSE | Online Coaching ...
Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Electric Charges And Fields | Toppers CBSE | Online Coaching ... Green functions in electrostatics represent the potential due to a unit source and are essential for solving boundary value problems. they encode the effects of boundary conditions, allowing for the calculation of potentials from charge distributions through integration. the discussion highlights confusion regarding the relationship between green functions and potentials, particularly when. The discussion focuses on the dimensions of the coulomb constant k in coulomb's law, which is expressed as k = 9.0 × 10^9 [nm²/c²] in mks units. participants debate whether k is dimensionless or has dimensions derived from fundamental quantities like mass, length, time, and charge. the conversation highlights the differences between mks and cgs units, noting that in cgs, the coulomb. It's pretty easy to disprove this idea, even on the level of newtonian gravity: first of all the sources of the electrostatic field are charge distributions at rest, those of the gravitational field are mass distributions, and in electrostatics like sign charges repell, while the always positive (i.e., like sign) masses attract each other. the deeper reason comes of course from relativity. In "classical electrodynamics 3rd ed.," j.d. jackson has an exercise, 1.10, to derive the mean value theorem of electrostatics. does anyone know of a derivation which is located on the web? pete.

Electrostatics: Electric Charges & Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes
Electrostatics: Electric Charges & Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes It's pretty easy to disprove this idea, even on the level of newtonian gravity: first of all the sources of the electrostatic field are charge distributions at rest, those of the gravitational field are mass distributions, and in electrostatics like sign charges repell, while the always positive (i.e., like sign) masses attract each other. the deeper reason comes of course from relativity. In "classical electrodynamics 3rd ed.," j.d. jackson has an exercise, 1.10, to derive the mean value theorem of electrostatics. does anyone know of a derivation which is located on the web? pete. The discussion revolves around calculating the work required to assemble four point charges into a tetrahedron. the initial attempt incorrectly included a factor of 1/2 in the work equation, which led to confusion regarding the correct answer. the correct approach involves summing the potential energy contributions from each charge without double counting interactions. it was clarified that. The discussion revolves around the electrostatic properties of scotch tape, particularly why the top piece is often considered negatively charged after separation. participants note that both pieces are plastic, which typically acquires a negative charge, but the charge distribution can vary based on handling and the materials involved. the interaction between the tape and surfaces, such as. The discussion explores the differences in electric fields between electrostatics and electrodynamics, particularly in conductors. in electrostatics, electric fields are time independent, zero inside conductors, and nonzero at their surfaces, while static magnetic fields can penetrate conductors. in electrodynamics, moving charges and time varying electric fields can create scenarios where a. The basic idea is that electrostatics is the study of static (unchanging) electric fields, electric charges, and the rules governing their interactions. magnetism is the study of static magnetic fields, magnets, and the rules for their interactions. the two areas are tied together with electrodynamics, which is the study of changing electric and magnetic fields and em waves.

Electrostatics Handwritten Notes For Class 12 Physics
Electrostatics Handwritten Notes For Class 12 Physics The discussion revolves around calculating the work required to assemble four point charges into a tetrahedron. the initial attempt incorrectly included a factor of 1/2 in the work equation, which led to confusion regarding the correct answer. the correct approach involves summing the potential energy contributions from each charge without double counting interactions. it was clarified that. The discussion revolves around the electrostatic properties of scotch tape, particularly why the top piece is often considered negatively charged after separation. participants note that both pieces are plastic, which typically acquires a negative charge, but the charge distribution can vary based on handling and the materials involved. the interaction between the tape and surfaces, such as. The discussion explores the differences in electric fields between electrostatics and electrodynamics, particularly in conductors. in electrostatics, electric fields are time independent, zero inside conductors, and nonzero at their surfaces, while static magnetic fields can penetrate conductors. in electrodynamics, moving charges and time varying electric fields can create scenarios where a. The basic idea is that electrostatics is the study of static (unchanging) electric fields, electric charges, and the rules governing their interactions. magnetism is the study of static magnetic fields, magnets, and the rules for their interactions. the two areas are tied together with electrodynamics, which is the study of changing electric and magnetic fields and em waves.

CBSE Class 12 Physics Notes : Electrostatics | AglaSem Schools
CBSE Class 12 Physics Notes : Electrostatics | AglaSem Schools The discussion explores the differences in electric fields between electrostatics and electrodynamics, particularly in conductors. in electrostatics, electric fields are time independent, zero inside conductors, and nonzero at their surfaces, while static magnetic fields can penetrate conductors. in electrodynamics, moving charges and time varying electric fields can create scenarios where a. The basic idea is that electrostatics is the study of static (unchanging) electric fields, electric charges, and the rules governing their interactions. magnetism is the study of static magnetic fields, magnets, and the rules for their interactions. the two areas are tied together with electrodynamics, which is the study of changing electric and magnetic fields and em waves.
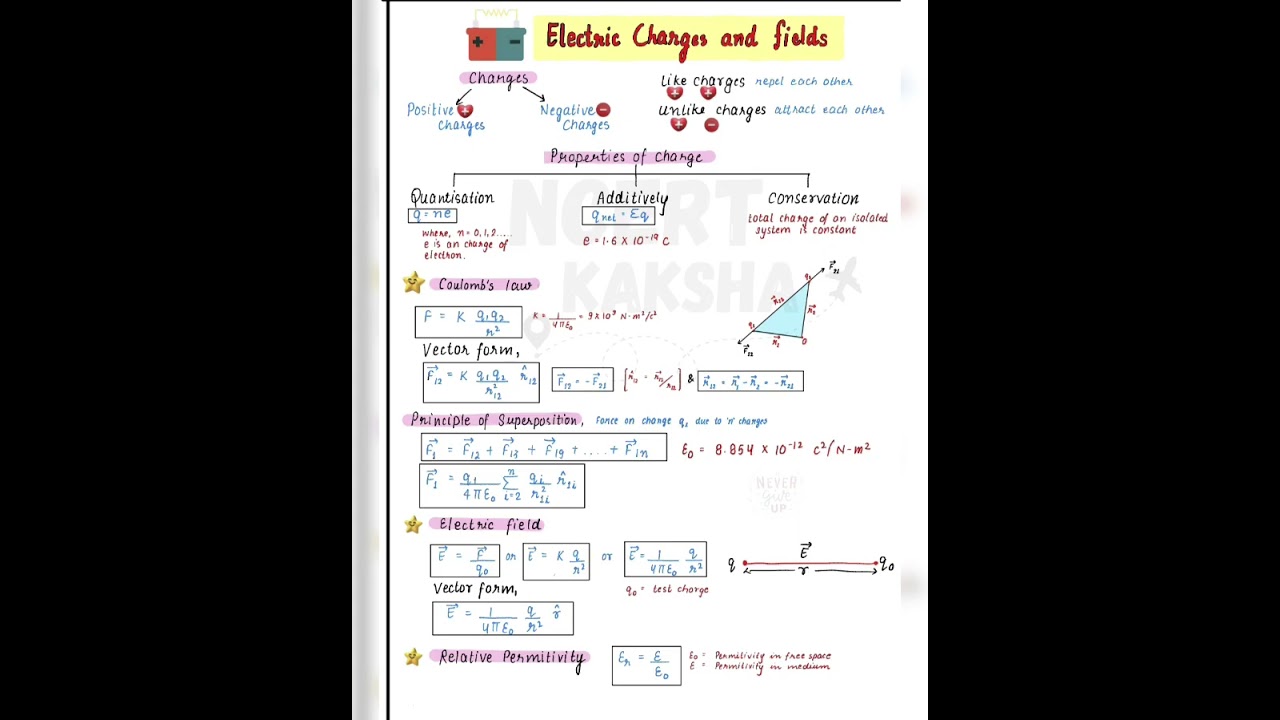
FORMULA SHEET OF PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CLASS 12 .... ELECTRIC CHARGE AND FIELD .. SUBSCRIBE FOR MORE .
FORMULA SHEET OF PHYSICS CHAPTER 1 CLASS 12 .... ELECTRIC CHARGE AND FIELD .. SUBSCRIBE FOR MORE .
Related image with electrostatics electric charges fields class 12 physics chapter 1 notes
Related image with electrostatics electric charges fields class 12 physics chapter 1 notes
About "Electrostatics Electric Charges Fields Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Notes"










![Electric Charges And Fields Class 12 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 1 [PDF] Electric Charges And Fields Class 12 Notes CBSE Physics Chapter 1 [PDF]](https://i0.wp.com/www.vedantu.com/content-images/revision-notes/cbse-class-12-physics-notes-chapter-1-electric-charges-and-fields/1.png?resize=91,91)





Comments are closed.