Momentum And Problem Solving Question 2

Problem Solving Momentum | PDF
Problem Solving Momentum | PDF When solving momentum problems, the first step is to assign a positive direction. then, compare the velocities in this direction. velocities in the same direction as the positive direction are considered to have positive momentum, while those in the opposite direction have negative momentum. We are solving for the final velocity of objects, when both object have the same final velocity.

Homework And Exercises - Momentum Conceptual Question - Physics Stack Exchange
Homework And Exercises - Momentum Conceptual Question - Physics Stack Exchange On this page i put together a collection of momentum problems to help you understand momentum better. the required equations and background reading to solve these problems is given on the momentum pages on the dynamics page. This collection of pages comprise worksheets in pdf format that developmentally target key concepts and mathematics commonly covered in a high school physics curriculum. Conservation of momentum implies that the total momentum in a system before an event (i. a collision) is the same as the total momentum after a collision. in elastic collisions, both kinetic energy and momentum are conserved. This page organizes the solved example problems that use momentum and force into several common categories. most problems appear in more than one category. an alphabetical list of momentum problems is shown in the table of contents in the left navigation bar.

Learn AP Physics - Momentum
Learn AP Physics - Momentum Conservation of momentum implies that the total momentum in a system before an event (i. a collision) is the same as the total momentum after a collision. in elastic collisions, both kinetic energy and momentum are conserved. This page organizes the solved example problems that use momentum and force into several common categories. most problems appear in more than one category. an alphabetical list of momentum problems is shown in the table of contents in the left navigation bar. Physics academic classroom practice 1. a 1300 kg race car is traveling at 80 m/s while a . 5,000 kg truck is traveling at . m/ . which has the greater momentum? 2. a 30. kg snowmobile is traveling at 30 m/s. how fast would a 200 kg snowmobile ne. to. travel to have the same momentum? 3. a loaded delivery truck has a . This section of the physics hypertextbook is a gathering place for momentum problems where the momentums are not necessarily pointing in convenient directions. Momentum can be described as the sum product of the mass of an object and its velocity. this means that momentum measures the force produced by an object’s mass and velocity. How does the momentum change if the truck is loaded with 1 200 kg and then travels at 60 km·h –1? solutions. the formula for momentum is p = mv , so the momentum will double and will be equal to 40 000 kg·m·s –1 in the same direction as before. ∴ v = 30 m·s –1 in the same direction as the momentum.

Solved Learning: Module 10: Linear Momentum QUESTION ANSWER | Chegg.com
Solved Learning: Module 10: Linear Momentum QUESTION ANSWER | Chegg.com Physics academic classroom practice 1. a 1300 kg race car is traveling at 80 m/s while a . 5,000 kg truck is traveling at . m/ . which has the greater momentum? 2. a 30. kg snowmobile is traveling at 30 m/s. how fast would a 200 kg snowmobile ne. to. travel to have the same momentum? 3. a loaded delivery truck has a . This section of the physics hypertextbook is a gathering place for momentum problems where the momentums are not necessarily pointing in convenient directions. Momentum can be described as the sum product of the mass of an object and its velocity. this means that momentum measures the force produced by an object’s mass and velocity. How does the momentum change if the truck is loaded with 1 200 kg and then travels at 60 km·h –1? solutions. the formula for momentum is p = mv , so the momentum will double and will be equal to 40 000 kg·m·s –1 in the same direction as before. ∴ v = 30 m·s –1 in the same direction as the momentum.

ProblemSet1 Momentum | PDF
ProblemSet1 Momentum | PDF Momentum can be described as the sum product of the mass of an object and its velocity. this means that momentum measures the force produced by an object’s mass and velocity. How does the momentum change if the truck is loaded with 1 200 kg and then travels at 60 km·h –1? solutions. the formula for momentum is p = mv , so the momentum will double and will be equal to 40 000 kg·m·s –1 in the same direction as before. ∴ v = 30 m·s –1 in the same direction as the momentum.

Past Paper Question Of Momentum 2 | PDF
Past Paper Question Of Momentum 2 | PDF
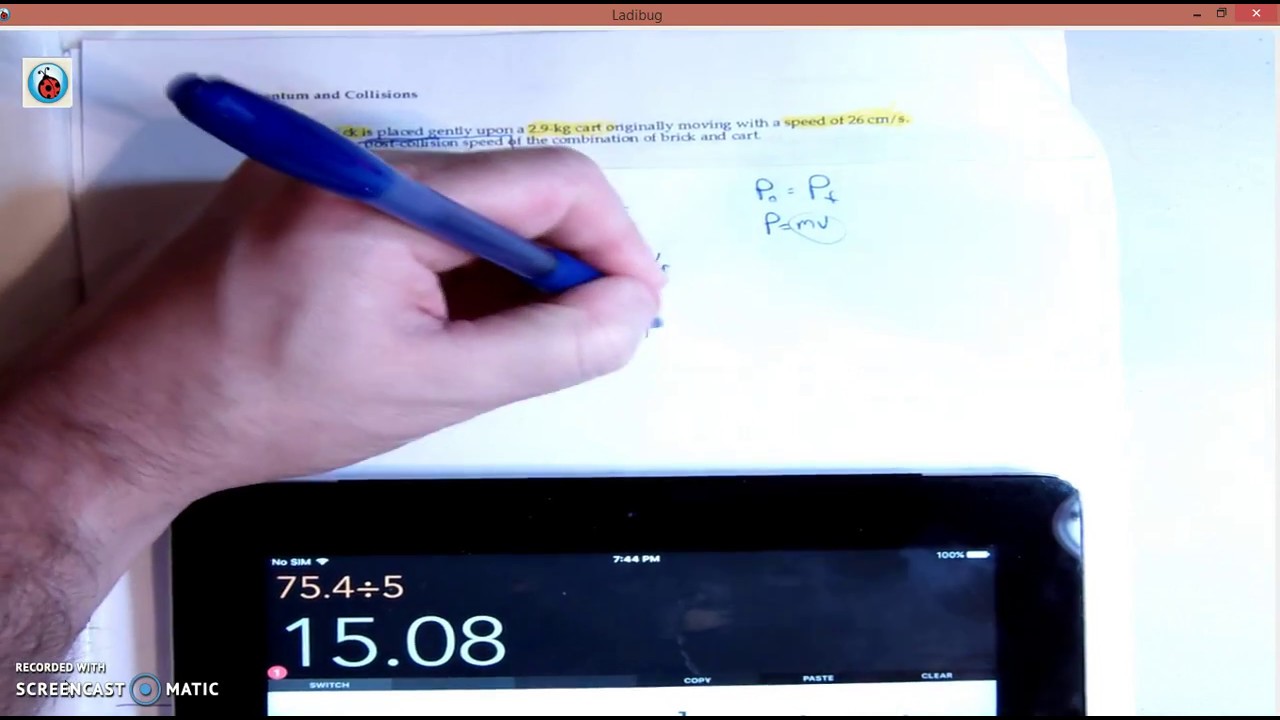
Momentum and Problem-Solving Question 2
Momentum and Problem-Solving Question 2
Related image with momentum and problem solving question 2
Related image with momentum and problem solving question 2
About "Momentum And Problem Solving Question 2"
















Comments are closed.