Normal Distributions And The Empirical Rule Mapleprimes

Empirical Rule Examples Normal Distribution Pdf Standard Deviation Statistics This post introduces you to normal distribution and some of its distinctive features. you'll also learn about empirical rule (or 68 95 99.7 rule), which dictates how values are spread in specific intervals around the mean. Empirical rule when a histogram of data is considered to meet the conditions of a “normal distribution”, (i.e. its graph is approximately bell shaped), then it is often possible to categorize the data using the following guidelines.

Normal Distribution Empirical Rule Pdf The empirical rule tells us that only about 5% of values in a normal distribution are more than two standard deviations from the mean. we will say that any value that is more than two standard deviations from the mean are considered unusual. The empirical rule consider the distributions shown below: all of them are normally distributed, but each has different variation (spread). for a normal distribution, we use the standard deviation to describe the variation, or spread of the data values around the mean. The "68–95–99.7 rule" is often used to quickly get a rough probability estimate of something, given its standard deviation, if the population is assumed to be normal. The empirical rule in statistics, also known as the 68 95 99 rule, states that for normal distributions, 68% of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean, 95% will fall within two standard deviations, and 99.7% will occur within three standard deviations.

Normal Distribution Empirical Rule The "68–95–99.7 rule" is often used to quickly get a rough probability estimate of something, given its standard deviation, if the population is assumed to be normal. The empirical rule in statistics, also known as the 68 95 99 rule, states that for normal distributions, 68% of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean, 95% will fall within two standard deviations, and 99.7% will occur within three standard deviations. First, we start with a normal distribution, symmetrical and bell shaped. the empirical rule is a rule telling us about where an observation lies in a normal distribution. The one property of normal distributions we’ll get into today is the empirical rule, also known as the 68 95 99.7 rule. it means that 68% of the distribution’s data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three. Early statisticians noticed the same shape coming up over and over again in different distributions—so they named it the normal distribution. it is symmetric about the mean. in other words, if you divide the graph in half by drawing a vertical line at the mean, there will be two identical halves. What is the empirical rule? the empirical rule summarizes the percentage of data from a normal distribution that falls within one, two, or three standard deviations of the mean. what are the requirements to use the empirical rule? your data should be normally distributed.
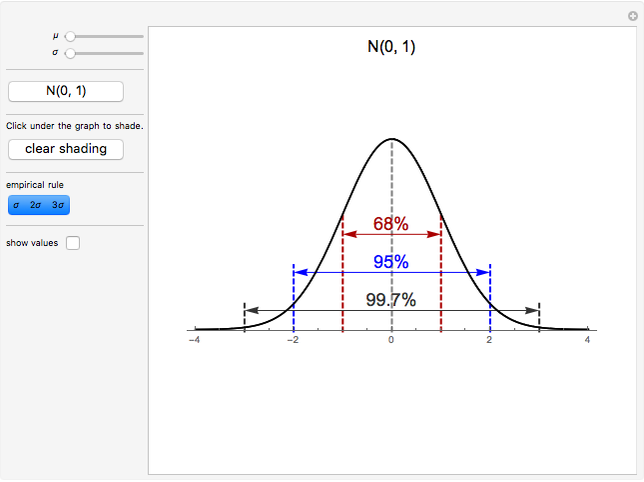
The Empirical Rule For Normal Distributions Wolfram Demonstrations Project First, we start with a normal distribution, symmetrical and bell shaped. the empirical rule is a rule telling us about where an observation lies in a normal distribution. The one property of normal distributions we’ll get into today is the empirical rule, also known as the 68 95 99.7 rule. it means that 68% of the distribution’s data falls within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three. Early statisticians noticed the same shape coming up over and over again in different distributions—so they named it the normal distribution. it is symmetric about the mean. in other words, if you divide the graph in half by drawing a vertical line at the mean, there will be two identical halves. What is the empirical rule? the empirical rule summarizes the percentage of data from a normal distribution that falls within one, two, or three standard deviations of the mean. what are the requirements to use the empirical rule? your data should be normally distributed.
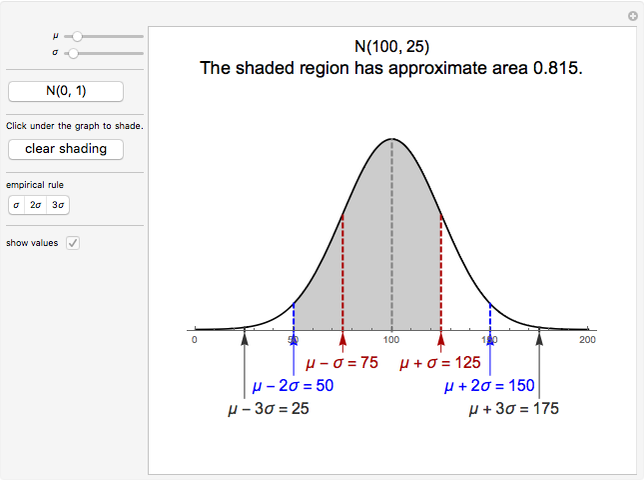
The Empirical Rule For Normal Distributions Wolfram Demonstrations Project Early statisticians noticed the same shape coming up over and over again in different distributions—so they named it the normal distribution. it is symmetric about the mean. in other words, if you divide the graph in half by drawing a vertical line at the mean, there will be two identical halves. What is the empirical rule? the empirical rule summarizes the percentage of data from a normal distribution that falls within one, two, or three standard deviations of the mean. what are the requirements to use the empirical rule? your data should be normally distributed.
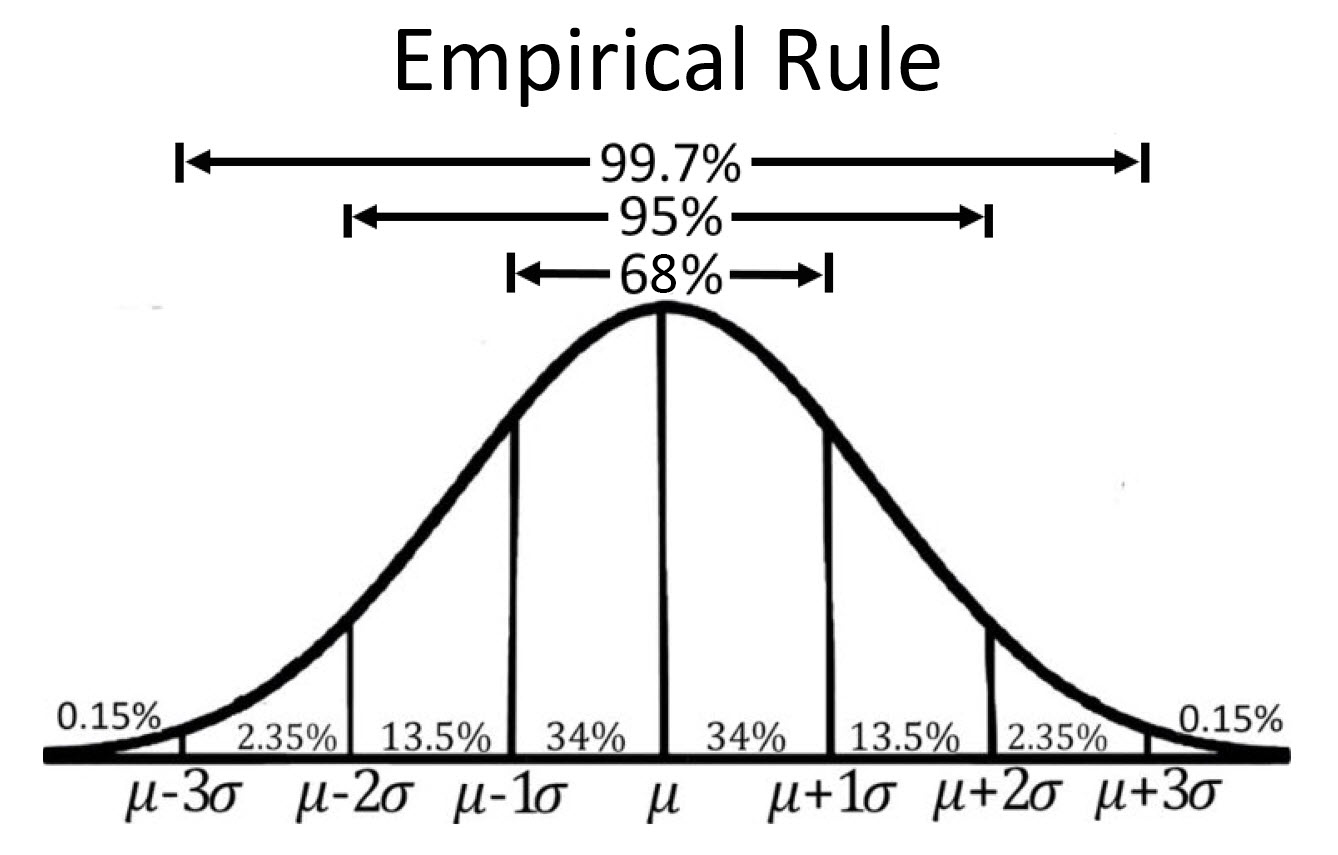
Normal Distribution Empirical Rule 68 95 99 7 Rule Andymath
Comments are closed.