Physical Science Module 1 Study Guide Problems

Physical Science Module 1 | PDF | Atoms | Atomic Nucleus
Physical Science Module 1 | PDF | Atoms | Atomic Nucleus What is newton's second law? the acceleration of an object depends directly upon the net force acting upon the object, and inversely upon the mass of the object., or more well know as force = acceleration x mass. Summarizes the contents of module 1, including the definitions of physical sciences, the wording of different types of scientific thought and the differences.

PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 1 Light And Heavy Elements Notes | PDF | Radioactive Decay | Nuclear Physics
PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 1 Light And Heavy Elements Notes | PDF | Radioactive Decay | Nuclear Physics Module 1 physical science dba notes motion & frame of reference~01.02 motion is defined as a change in position of an object relative to frame of reference aframe of reference (reference point) is a place or object that you assume is fixed. The test will cover concepts from the physical science chapter including energy, force, mass, matter, and the phases of matter. it will consist of modified true/false questions, fill in the blank, short answer, dimensional analysis problems, and essay items. Sound travels around corners because it has larger wavelengths than light, which is why we can hear sounds around corners, but we can't see around corners because light has a very small wavelength. interference: the result of overlapping. waves can meet, share space, and pass through each other. image credit: clarks science. 1. closed system: nothing goes in or out that affects the system example: bathtub of water considered closed system if no water goes in or out (plugged) 2. open system: something coming in from the outside or something leaves the system affects it. example: if the drain didn’t close in the bathtub; water would run out; open system how science.

Physical Science Module 1.pdf
Physical Science Module 1.pdf Sound travels around corners because it has larger wavelengths than light, which is why we can hear sounds around corners, but we can't see around corners because light has a very small wavelength. interference: the result of overlapping. waves can meet, share space, and pass through each other. image credit: clarks science. 1. closed system: nothing goes in or out that affects the system example: bathtub of water considered closed system if no water goes in or out (plugged) 2. open system: something coming in from the outside or something leaves the system affects it. example: if the drain didn’t close in the bathtub; water would run out; open system how science. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like scientific theory, what are some questions that an experiment can answer?, how do you test a hypothesis? and more. Review the buoyancy and density problems located at the end of your submarine lab. write the question that you most struggled with and the best answer you could make to it now. Study flashcards on physical science module:1 study guide at cram.com. quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you want!. It includes sections on cycles of matter, momentum, newton's laws, chemical bonding, and various physical science principles, along with questions and prompts for students to fill out.
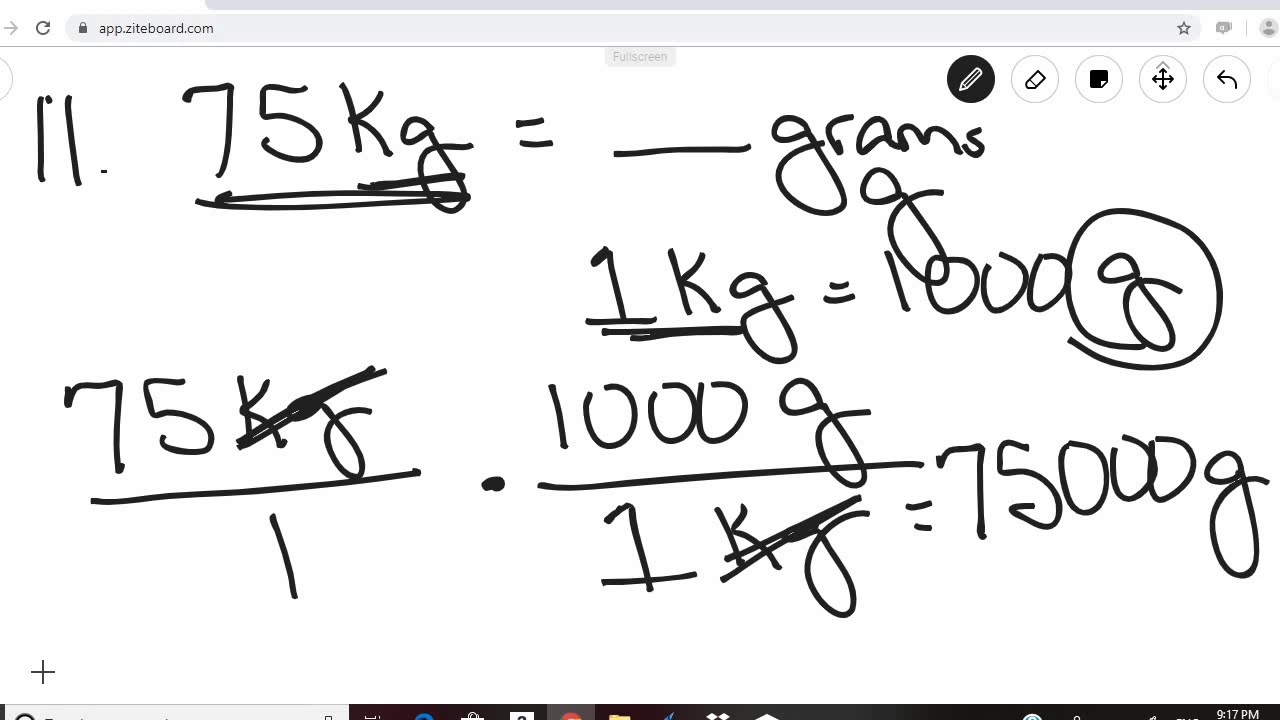
Physical Science Module 1 Study Guide Problems
Physical Science Module 1 Study Guide Problems
Related image with physical science module 1 study guide problems
Related image with physical science module 1 study guide problems
About "Physical Science Module 1 Study Guide Problems"
















Comments are closed.