Ppt 1 Of Chapter 2 Sample Space Probability And Addition Rule Of Probability Pdf

PPT-1 Of Chapter 2 Sample Space, Probability And Addition Rule Of Probability | PDF ...
PPT-1 Of Chapter 2 Sample Space, Probability And Addition Rule Of Probability | PDF ... Ppt 1 of chapter 2 sample space, probability and addition rule of probability free download as powerpoint presentation (.ppt / .pptx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Note: the term sample space reflects the fact that, in statistics, the sible outcomes often consists of the possible samples of a given size, as table 4.2 on page 145.

Probability Part 2 | PDF | Probability | Probability And Statistics
Probability Part 2 | PDF | Probability | Probability And Statistics It provides examples of how to calculate probabilities of simple and compound events using classical probability methods, including determining probabilities using fractions or decimals and interpreting "and" and "or" probabilities. download as a pptx, pdf or view online for free. Here are the course lecture notes for the course mas108, probability i, at queen mary, university of london, taken by most mathematics students and some others in the first semester. When a sample space can be constructed in several steps or stages, we can represent each of the n1 ways of completing the first step as a branch of a tree. This intuitive idea can formalize with the following probability rule: p(a or b)= p(a) p(b) – p(a and b) p(h or f)= p(h) p(f) – p(h and f) where p(a and b) denotes the probability that event a and event b happen at the same time.

3 Elementary Probability-Slides | PDF | Set (Mathematics) | Probability
3 Elementary Probability-Slides | PDF | Set (Mathematics) | Probability When a sample space can be constructed in several steps or stages, we can represent each of the n1 ways of completing the first step as a branch of a tree. This intuitive idea can formalize with the following probability rule: p(a or b)= p(a) p(b) – p(a and b) p(h or f)= p(h) p(f) – p(h and f) where p(a and b) denotes the probability that event a and event b happen at the same time. Learn about sample spaces, events, conditional probability, counting techniques, and laws in probability theory. understand how to interpret and calculate probabilities of events. This document discusses basic concepts of probability, including: the addition rule and multiplication rule for calculating probabilities of compound events. events can be disjoint (mutually exclusive) or not disjoint. Probability is a measure of one's belief in the occurrence of a future event. the subject of probability theory is the foundation upon which all of statistics is built, providing a means for modeling populations, experiments, or almost anything else that could be considered a random phenomenon. A random sample of 500 people who participated in the 2000 census was chosen. each member of the sample was identified as a high school graduate (or not) and as a homeowner (or not).

Sample Space And Probability (Geometric Probability Included) Guided Notes
Sample Space And Probability (Geometric Probability Included) Guided Notes Learn about sample spaces, events, conditional probability, counting techniques, and laws in probability theory. understand how to interpret and calculate probabilities of events. This document discusses basic concepts of probability, including: the addition rule and multiplication rule for calculating probabilities of compound events. events can be disjoint (mutually exclusive) or not disjoint. Probability is a measure of one's belief in the occurrence of a future event. the subject of probability theory is the foundation upon which all of statistics is built, providing a means for modeling populations, experiments, or almost anything else that could be considered a random phenomenon. A random sample of 500 people who participated in the 2000 census was chosen. each member of the sample was identified as a high school graduate (or not) and as a homeowner (or not).

(PDF) Chapter 2 PROBABILITY SAMPLE SPACEbrahms.emu.edu.tr/Math322/Lecture Notes/Math322 Chapter ...
(PDF) Chapter 2 PROBABILITY SAMPLE SPACEbrahms.emu.edu.tr/Math322/Lecture Notes/Math322 Chapter ... Probability is a measure of one's belief in the occurrence of a future event. the subject of probability theory is the foundation upon which all of statistics is built, providing a means for modeling populations, experiments, or almost anything else that could be considered a random phenomenon. A random sample of 500 people who participated in the 2000 census was chosen. each member of the sample was identified as a high school graduate (or not) and as a homeowner (or not).

Chapter2 Probability PDF | PDF | Probability | Experiment
Chapter2 Probability PDF | PDF | Probability | Experiment
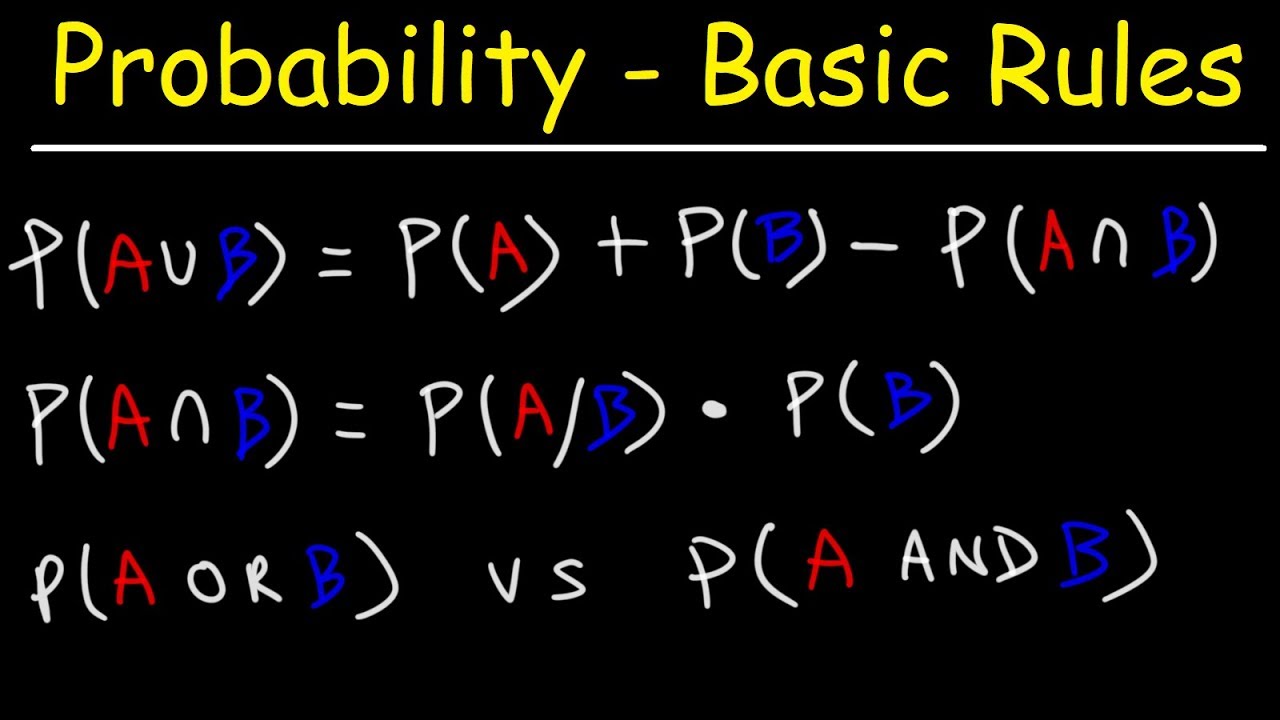
Multiplication & Addition Rule - Probability - Mutually Exclusive & Independent Events
Multiplication & Addition Rule - Probability - Mutually Exclusive & Independent Events
Related image with ppt 1 of chapter 2 sample space probability and addition rule of probability pdf
Related image with ppt 1 of chapter 2 sample space probability and addition rule of probability pdf
About "Ppt 1 Of Chapter 2 Sample Space Probability And Addition Rule Of Probability Pdf"
















Comments are closed.