Probabilities Of Mutually Exclusive Non Mutually Exclusive Events

Mutually And Non Mutually Exclusive Events Pdf Probability Linguistics The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur. [note 1][1][2] this number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. a simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. How likely something is to happen. many events can't be predicted with total certainty. the best we can say is how likely they are to happen, using the idea of probability. when a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes: also: when a single die is thrown, there are six possible outcomes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.

Calculating Probabilities Of Mutually Exclusive And Non Exclusive Events Pdf Teaching The probabilities of events that are certain or impossible are easy to assign; they’re just 1 or 0, respectively. what do we do about those in between cases, for events that might or might not occur?. Probability defines the likelihood of occurrence of an event. there are many real life situations in which we may have to predict the outcome of an event. we may be sure or not sure of the results of an event. in such cases, we say that there is a probability of this event to occur or not occur. Learn about real world uses for probabilities, how to calculate them, and the two main branches of probability theory. Probability is the likelihood of an event occurring. to calculate the probability of an event happening, use the formula. for example, let’s look at the probability of getting an even number when a fair die is rolled. the desired outcome is getting an even number. there are 3 even numbers on a die.

Probability Of Mutually Exclusive Events Pdf Probability Probability Theory Learn about real world uses for probabilities, how to calculate them, and the two main branches of probability theory. Probability is the likelihood of an event occurring. to calculate the probability of an event happening, use the formula. for example, let’s look at the probability of getting an even number when a fair die is rolled. the desired outcome is getting an even number. there are 3 even numbers on a die. Probability is defined as the measure of how likely an event is to happen, usually expressed as a value between zero and one. a probability of zero indicates that the event is impossible, while a probability of one signifies absolute certainty. We know the probabilities of each outcome, so we can compute the probabilities of events! in this case, each of the six outcomes in the event [marilyn wins] occurs with probability 1 9, so pr[marilyn wins] = 6 9 = 2 3. There are three major types of probabilities: it is based on the possible chances of something to happen. Probability tells us how likely it is that something will happen. find out about fractions and probability in this bitesize ks2 maths guide.
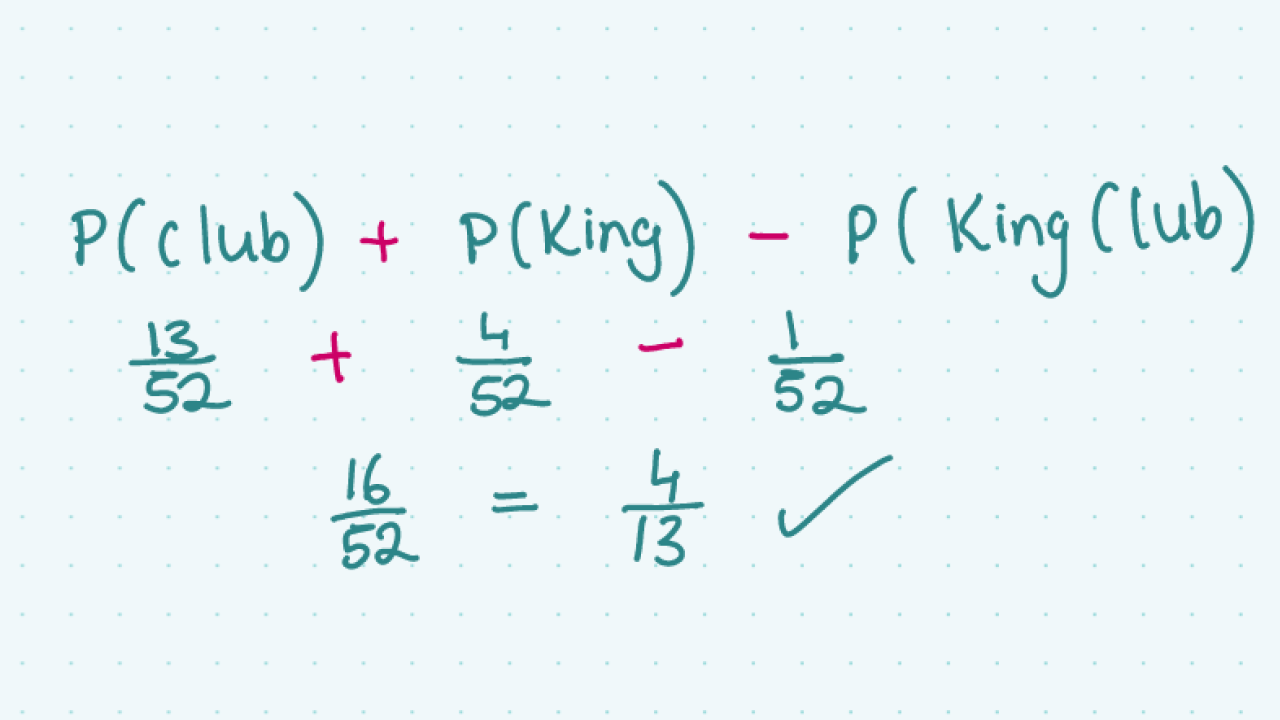
Non Mutually Exclusive Events Studyclix Probability is defined as the measure of how likely an event is to happen, usually expressed as a value between zero and one. a probability of zero indicates that the event is impossible, while a probability of one signifies absolute certainty. We know the probabilities of each outcome, so we can compute the probabilities of events! in this case, each of the six outcomes in the event [marilyn wins] occurs with probability 1 9, so pr[marilyn wins] = 6 9 = 2 3. There are three major types of probabilities: it is based on the possible chances of something to happen. Probability tells us how likely it is that something will happen. find out about fractions and probability in this bitesize ks2 maths guide.

Mutually Exclusive Vs Non Mutually Exclusive Event Probability By Master3du There are three major types of probabilities: it is based on the possible chances of something to happen. Probability tells us how likely it is that something will happen. find out about fractions and probability in this bitesize ks2 maths guide.
Comments are closed.