Refrigerator Heatpump Pdf Heat Heat Pump

Refrigerator Heatpump | PDF | Heat | Heat Pump
Refrigerator Heatpump | PDF | Heat | Heat Pump Different from refrigerators, the main purpose of heat pumps is to add heat, q ˙ h, to a heat source, such as an indoor space of a building. therefore, we are interested in the amount of heat, q ˙ h, that can be transferred from the condenser to the heat source per unit power consumption. Describe how heat engines operate as heat pumps and refrigerators. explain how a heat pump transfers thermal energy into an interior space. distinguish between the function of heat pumps and refrigerators. calculate the coefficient of performance (cop) of a heat pump.

Thermo Heat Pump | PDF | Heat Pump | Hvac
Thermo Heat Pump | PDF | Heat Pump | Hvac Either a refrigerator or a heat pump is an engine running in reverse. for a refrigerator, the focus is on removing heat from a specific area. for a heat pump, the focus is on dumping heat to a specific area. we first consider a refrigerator (figure \ (\pageindex {1}\)). Heat pump systems offer an alternative to furnaces and air conditioners in climates with moderate heating and cooling needs. the most common type of heat pump is the air source heat pump, which transfers heat between your house and the outside air. Heat pumps and refrigerators are systems that utilize thermodynamic cycles to "pump" heat from a cold source to a warm source. heat pumps can be designed using a traditional vapor. Heat pumps offer an energy efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners for all climates. like your refrigerator, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, making the cool space cooler and the warm space warmer.

UNIT - II Heat Engine, Refrigerator And Heat Pump | PDF | Heat | Thermodynamics
UNIT - II Heat Engine, Refrigerator And Heat Pump | PDF | Heat | Thermodynamics Heat pumps and refrigerators are systems that utilize thermodynamic cycles to "pump" heat from a cold source to a warm source. heat pumps can be designed using a traditional vapor. Heat pumps offer an energy efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners for all climates. like your refrigerator, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, making the cool space cooler and the warm space warmer. The key differences are that a refrigerator operates between a cold body temperature and atmospheric temperature, a heat pump operates between hot and atmospheric temperatures, and a heat engine converts heat into work. the performance of each is measured by their coefficient of performance (cop). we take content rights seriously. Just a heat engine run backwards note that this means you can get almost 12 times the heat energy than you are supplying in the form of work!. Any refrigerating system is a heat pump, which extracts heat from a cold body and delivers it to a hot body. thus there is no difference in the operation cycle of a refrigerator and a heat pump. the main difference between them is in their operating temperatures. Heat pumps, refrigerators, and bricks! heat is transferred from cold to hot by action of work on the engine. note that heat never flows spontaneously from cold to hot; the cold gas is being heated by adiabatic compression (process 3). = t c/ t h is still true. (note: qh, qc, and w are still positive!) pumps are heat engines running in reverse.

Refrigeration & Heat Pump Principles, The Basics - ECAC
Refrigeration & Heat Pump Principles, The Basics - ECAC The key differences are that a refrigerator operates between a cold body temperature and atmospheric temperature, a heat pump operates between hot and atmospheric temperatures, and a heat engine converts heat into work. the performance of each is measured by their coefficient of performance (cop). we take content rights seriously. Just a heat engine run backwards note that this means you can get almost 12 times the heat energy than you are supplying in the form of work!. Any refrigerating system is a heat pump, which extracts heat from a cold body and delivers it to a hot body. thus there is no difference in the operation cycle of a refrigerator and a heat pump. the main difference between them is in their operating temperatures. Heat pumps, refrigerators, and bricks! heat is transferred from cold to hot by action of work on the engine. note that heat never flows spontaneously from cold to hot; the cold gas is being heated by adiabatic compression (process 3). = t c/ t h is still true. (note: qh, qc, and w are still positive!) pumps are heat engines running in reverse.

Heat Pump Schematic Diagram
Heat Pump Schematic Diagram Any refrigerating system is a heat pump, which extracts heat from a cold body and delivers it to a hot body. thus there is no difference in the operation cycle of a refrigerator and a heat pump. the main difference between them is in their operating temperatures. Heat pumps, refrigerators, and bricks! heat is transferred from cold to hot by action of work on the engine. note that heat never flows spontaneously from cold to hot; the cold gas is being heated by adiabatic compression (process 3). = t c/ t h is still true. (note: qh, qc, and w are still positive!) pumps are heat engines running in reverse.
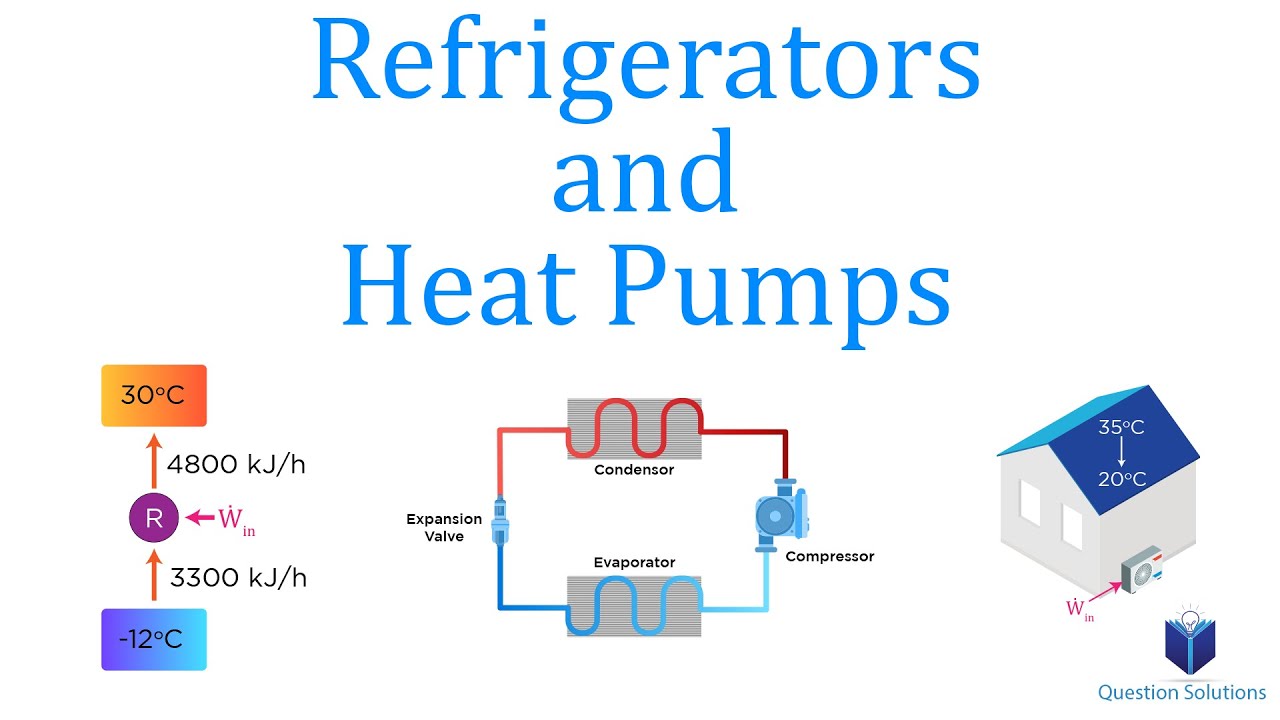
How Do Refrigerators and Heat Pumps Work? | Thermodynamics | (Solved Examples)
How Do Refrigerators and Heat Pumps Work? | Thermodynamics | (Solved Examples)
Related image with refrigerator heatpump pdf heat heat pump
Related image with refrigerator heatpump pdf heat heat pump
About "Refrigerator Heatpump Pdf Heat Heat Pump"







![[DIAGRAM] Heat Pump Refrigerant Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE [DIAGRAM] Heat Pump Refrigerant Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://i0.wp.com/ytimg.googleusercontent.com/vi/W8DK8hpnFkQ/maxresdefault.jpg?resize=91,91)







Comments are closed.