Scientists Discover How Human Brains Grow Larger Than Other Apes
Do Humans Have Big Brains Ask An Anthropologist Human brain cells take longer to mature than those of apes, giving them more time to divide and produce neurons. this delay is regulated by the gene zeb2, which may explain why human brains are so much larger. Now scientists from the mrc laboratory of molecular biology in cambridge think they know why: a gene called zeb2, which affects how cells move, kicks in later in human brains, giving us extra time to make extra brain matter.

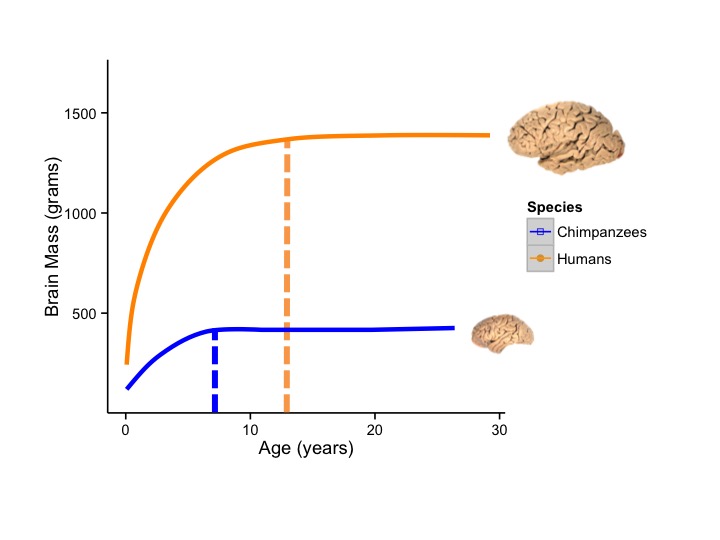
Scientists Discover How Human Brains Grow Larger Than Other Apes Results show that human neural progenitor stem cells took approximately a week to mature, compared to five days in primates. researchers believe this slower maturation allows for an increased quantity of neurons, which ultimately leads to larger human brains. But for fundamental questions about our evolution, these brain tissues in a dish provide an unprecedented view into key stages of brain development that would be impossible to study otherwise. How humans develop larger brains than other apes – a new study is the first to identify how human brains grow much larger, with three times as many neurons, compared with chimpanzee and gorilla brains. Using lab grown mini brains, scientists have figured out why humans have bigger brains than those of apes. about 5 million to 8 million years ago, humans and apes diverged from a common ancestor.

Scientists Discover How Humans Develop Much Larger Brains Than Other Apes How humans develop larger brains than other apes – a new study is the first to identify how human brains grow much larger, with three times as many neurons, compared with chimpanzee and gorilla brains. Using lab grown mini brains, scientists have figured out why humans have bigger brains than those of apes. about 5 million to 8 million years ago, humans and apes diverged from a common ancestor. To uncover the genetic mechanism driving these differences, the researchers compared gene expression which genes are turned on and off in the human brain organoids versus the other apes. Miniature brains of humans, gorillas and chimpanzees developed in the lab have shown how our brains grow much larger than those of other apes. at birth, our brains have around three times as many. Using brain organoid models, researchers have identified how the brain grows much larger and has three times as many neurons, as the brains of chimpanzees and gorillas. What is it about humans that separates us from non human primates, our closest living relatives? one of the biggest differentiators, scientifically speaking, is the size of our much larger brains – and now, we've found a key secret behind that unrivaled growth.
Comments are closed.