Solve The Initial Value Problem Y Cy 12 With Y0 0 To Solve This We Should Use The S

Answered: ¹) Solve The Initial Value Problem Yy'… | Bartleby
Answered: ¹) Solve The Initial Value Problem Yy'… | Bartleby The point: an introduction to numerical methods for solving initial value problems. the focus here is on the fundamental theory and concepts of stability and convergence. The calculator will try to find the solution of the given ode: first order, second order, nth order, separable, linear, exact, bernoulli, homogeneous, or inhomogeneous. initial conditions are also supported. for example, y'' (x) 25y (x)=0, y (0)=1, y' (0)=2.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Y' = (x + Y - 1)^2 | Chegg.com
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Y' = (x + Y - 1)^2 | Chegg.com Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. for math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music…. This calculus video tutorial explains how to solve the initial value problem as it relates to separable differential equations. more. As we dive into this article, we aim to unravel the mysterious process of solving initial value problems in differential equations. this article offers an immersive experience to newcomers intrigued by calculus’s wonders and experienced mathematicians looking for a comprehensive refresher. Thus, y = x3 − x2 2 is a solution of the differential equation that satisfies the given condition. in fact, it is the only solution that satisfies the condition since the general solution represented all solutions of the equation and the constant c was uniquely determined.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Y' = (x + Y - 1)2 | Chegg.com
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem Y' = (x + Y - 1)2 | Chegg.com As we dive into this article, we aim to unravel the mysterious process of solving initial value problems in differential equations. this article offers an immersive experience to newcomers intrigued by calculus’s wonders and experienced mathematicians looking for a comprehensive refresher. Thus, y = x3 − x2 2 is a solution of the differential equation that satisfies the given condition. in fact, it is the only solution that satisfies the condition since the general solution represented all solutions of the equation and the constant c was uniquely determined. We look at techniques for integrating a large variety of functions involving products, quotients, and compositions later in the text. here we turn to one common use for antiderivatives that arises often in many applications: solving differential equations. An initial value problem (ivp) is a differential equations problem in which we’re asked to use some given initial condition, or set of conditions, in order to find the particular solution to the differential equation. Here’s how to approach this question to start solving the initial value problem y ″ 7 y ′ 12 y = 0, y (0) = 1, y ′ (0) = 0, substitute y = e m x into the differential equation, transforming it into a characteristic equation. Suppose d = [a; b] r, a function f is continuous on d and lipschitz with respect to y, then the initial value problem y0 = f (t; y) for t 2 [a; b] with initial value y(a) = has a unique solution y(t) for t 2 [a; b].
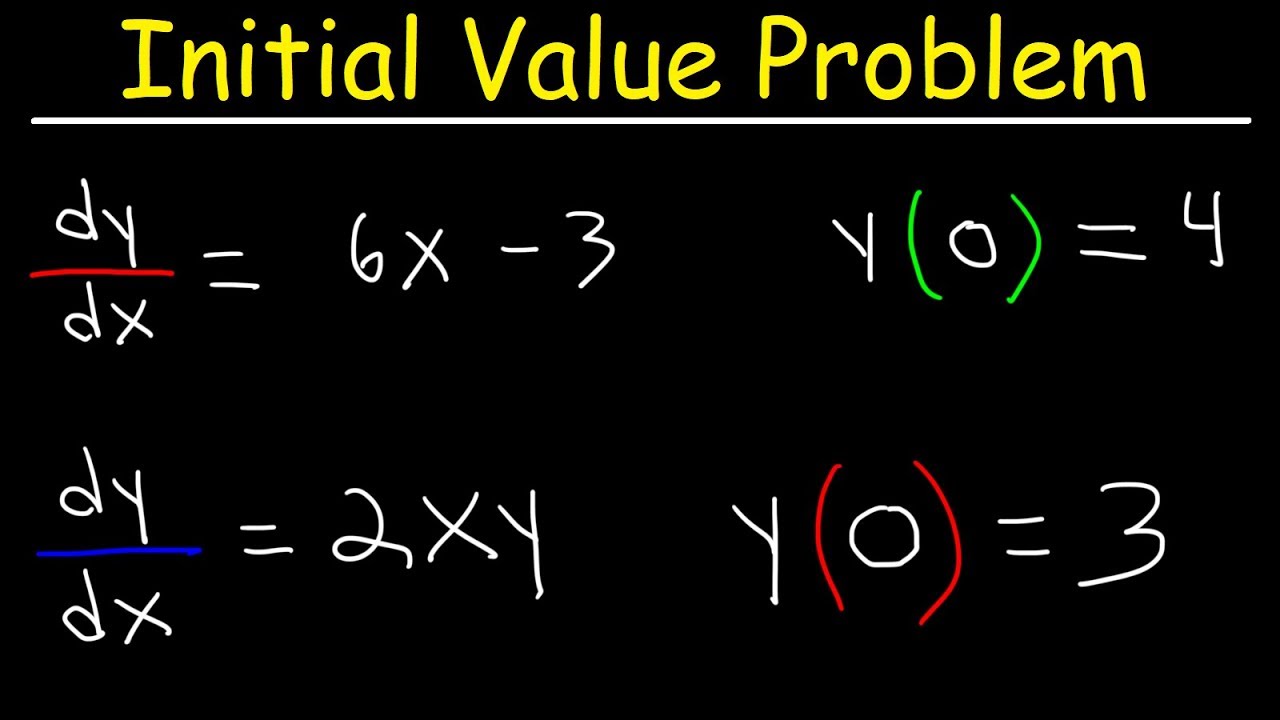
Initial Value Problem
Initial Value Problem
Related image with solve the initial value problem y cy 12 with y0 0 to solve this we should use the s
Related image with solve the initial value problem y cy 12 with y0 0 to solve this we should use the s
About "Solve The Initial Value Problem Y Cy 12 With Y0 0 To Solve This We Should Use The S"















Comments are closed.