Solved Problem 2solve The Following Initial Value Chegg Com

Solved Solve The Following Initial Value Problem. | Chegg.com
Solved Solve The Following Initial Value Problem. | Chegg.com Answer to #5) solve the following initial value problems. There are 3 steps to solve this one. consider the following initial value problem. finding the laplace transform of the solution of the gi not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem. Find The Solution Of | Chegg.com
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem. Find The Solution Of | Chegg.com Use laplace transforms to solve the initial value problem x′′ − 6x′ 8x = 2 x(0) = x′(0) = 0. solution using the formula for taking the laplace transform of a derivative, we get that the laplace transform of the left side of the differential equation is: (s2x(s) − sx(0) − x′(0)) − 6(sx(s) − x(0)) 8x(s). A) to solve this, we should use the substitution. enter derivatives using prime notation (e.g., you would enter for ). b) after the substitution from the previous part, we obtain the following linear differential equation in . c) the solution to the original initial value problem is described by the following equation in . To solve the initial value problem, we need to find the general solution to the system of differential equations and then apply the initial conditions to determine the specific solution. An initial value problem is a differential equation (i.e., an equation involving f ′) combined with an initial condition (i.e., f (a) = b). the goal of an initial value problem is to find the unique function that satisfies the differential equation and the initial condition.

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem. Find The Solution Of | Chegg.com
Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem. Find The Solution Of | Chegg.com To solve the initial value problem, we need to find the general solution to the system of differential equations and then apply the initial conditions to determine the specific solution. An initial value problem is a differential equation (i.e., an equation involving f ′) combined with an initial condition (i.e., f (a) = b). the goal of an initial value problem is to find the unique function that satisfies the differential equation and the initial condition. Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. solve the initial value problem. there are 4 steps to solve this one. Problem \# 1: solve the following initial value problem. y1′=−6y1 y2y2′=−6y1−y2y1 (0)=1,y2 (0)=3. enter the functions y1 (x) and y2 (x) (in that order) into the answer box below, separated with a comma. We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. We look at techniques for integrating a large variety of functions involving products, quotients, and compositions later in the text. here we turn to one common use for antiderivatives that arises often in many applications: solving differential equations.

Solved 5. Solve The Following Initial Value Problem: | Chegg.com
Solved 5. Solve The Following Initial Value Problem: | Chegg.com Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. solve the initial value problem. there are 4 steps to solve this one. Problem \# 1: solve the following initial value problem. y1′=−6y1 y2y2′=−6y1−y2y1 (0)=1,y2 (0)=3. enter the functions y1 (x) and y2 (x) (in that order) into the answer box below, separated with a comma. We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. We look at techniques for integrating a large variety of functions involving products, quotients, and compositions later in the text. here we turn to one common use for antiderivatives that arises often in many applications: solving differential equations.

Solved 1.Solve The Initial Value Problem 2.Solve The Initial | Chegg.com
Solved 1.Solve The Initial Value Problem 2.Solve The Initial | Chegg.com We can use laplace transforms to transform an initial value problem into an algebraic equation. once the algebraic equation is solved, we can use the inverse transform to obtain the solution to our original initial value problem. We look at techniques for integrating a large variety of functions involving products, quotients, and compositions later in the text. here we turn to one common use for antiderivatives that arises often in many applications: solving differential equations.
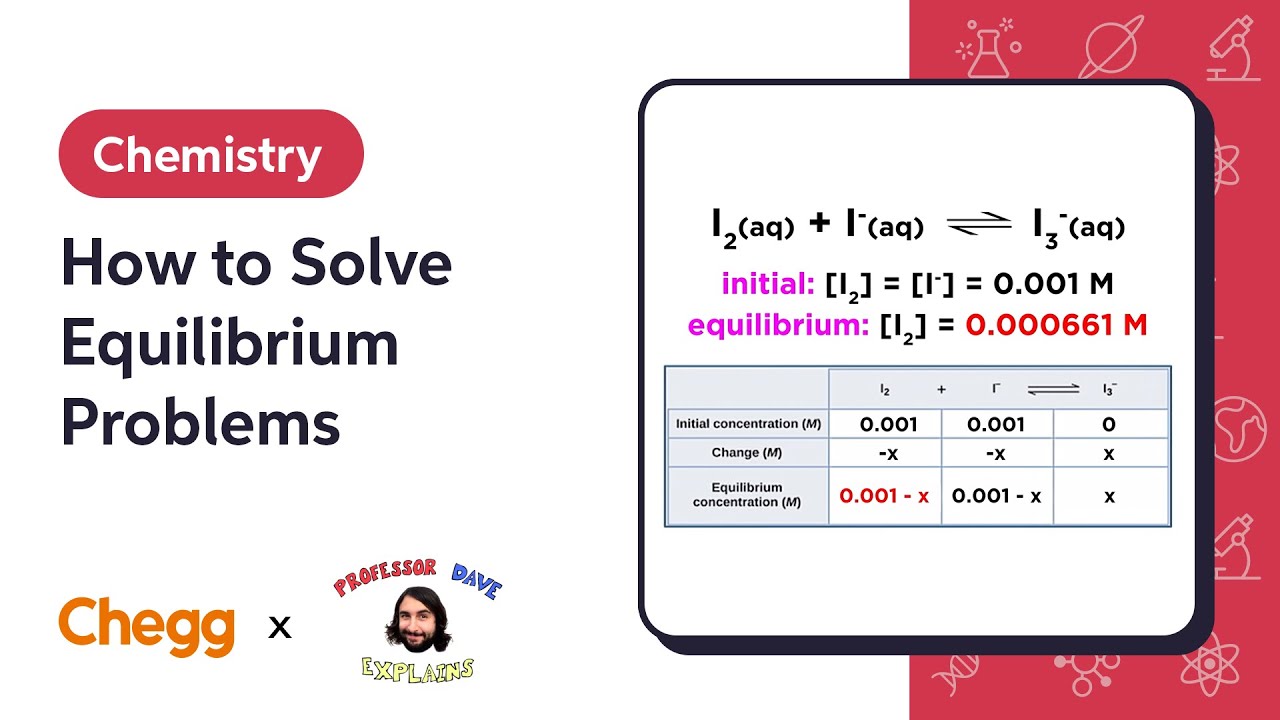
How to Solve Equilibrium Problems | Professor Dave & Chegg Explain
How to Solve Equilibrium Problems | Professor Dave & Chegg Explain
Related image with solved problem 2solve the following initial value chegg com
Related image with solved problem 2solve the following initial value chegg com
About "Solved Problem 2solve The Following Initial Value Chegg Com"





![Solved [1] Solve The Following Initial Value Problem: | Chegg.com Solved [1] Solve The Following Initial Value Problem: | Chegg.com](https://i0.wp.com/media.cheggcdn.com/media/b7a/b7a770fe-6945-412d-be29-0542a968ffa3/phpFtqAV0?resize=91,91)









Comments are closed.