Standard Form Quadratic Function

Quadratic Function Standard Form
Quadratic Function Standard Form What is the standard form of quadratic function? a quadratic function is a function that involves quadratic expression. i.e., its equation in standard form is f (x) = ax 2 bx c, where a ≠ 0. We know that the standard form of a quadratic equation is ax2 bx c = 0 and the vertex form is a (x p) (x q) = 0 where (p, 0) and (q, 0) are the x intercept and y intercept respectively.

40 Standard Form Quadratic Equation Images, Stock Photos & Vectors | Shutterstock
40 Standard Form Quadratic Equation Images, Stock Photos & Vectors | Shutterstock Learn how to graph any quadratic function that is given in standard form. here, sal graphs y=5x² 20x 15. created by sal khan. Standard form the standard form of a quadratic equation looks like this: a, b and c are known values. a can't be 0 x is the variable or unknown (we don't know it yet) here are some examples:. This article takes you on a comprehensive journey through the quadratic standard form. we will explain the role of each coefficient, walk through converting from vertex and factored representations, delve into graph interpretation, and boost your understanding of various solution techniques. Read below for an explanation of the three main forms of quadratics (standard form, factored form, and vertex form), examples of each form, as well as strategies for converting between the various quadratic forms. your mathematics journey has taken you far.

Standard Form Of A Quadratic Function
Standard Form Of A Quadratic Function This article takes you on a comprehensive journey through the quadratic standard form. we will explain the role of each coefficient, walk through converting from vertex and factored representations, delve into graph interpretation, and boost your understanding of various solution techniques. Read below for an explanation of the three main forms of quadratics (standard form, factored form, and vertex form), examples of each form, as well as strategies for converting between the various quadratic forms. your mathematics journey has taken you far. Write the vertex form of a quadratic function. y = a (x h) 2 k. square the binomial. y = a (x 2 2xh h 2) k. y = ax 2 2ahx ah 2 k. the equation y = ax 2 2axh ah 2 k is a quadratic function in standard form with. a = a. b = 2ah. c = ah 2 k. Learn about quadratic equations in standard form. read on to see how to convert quadratic equations to standard, vertex and intercept forms with examples for each. The standard form and the general form are equivalent methods of describing the same function. we can see this by expanding out the general form and setting it equal to the standard form. Once you finish the present tutorial, you may want to go through another tutorial on graphing quadratic functions. this form of the quadratic function is also called the vertex form. the term (x h) 2 is a square, hence is either positive or equal to zero.

How To Write Quadratic Function In Standard Form | Vondy
How To Write Quadratic Function In Standard Form | Vondy Write the vertex form of a quadratic function. y = a (x h) 2 k. square the binomial. y = a (x 2 2xh h 2) k. y = ax 2 2ahx ah 2 k. the equation y = ax 2 2axh ah 2 k is a quadratic function in standard form with. a = a. b = 2ah. c = ah 2 k. Learn about quadratic equations in standard form. read on to see how to convert quadratic equations to standard, vertex and intercept forms with examples for each. The standard form and the general form are equivalent methods of describing the same function. we can see this by expanding out the general form and setting it equal to the standard form. Once you finish the present tutorial, you may want to go through another tutorial on graphing quadratic functions. this form of the quadratic function is also called the vertex form. the term (x h) 2 is a square, hence is either positive or equal to zero.
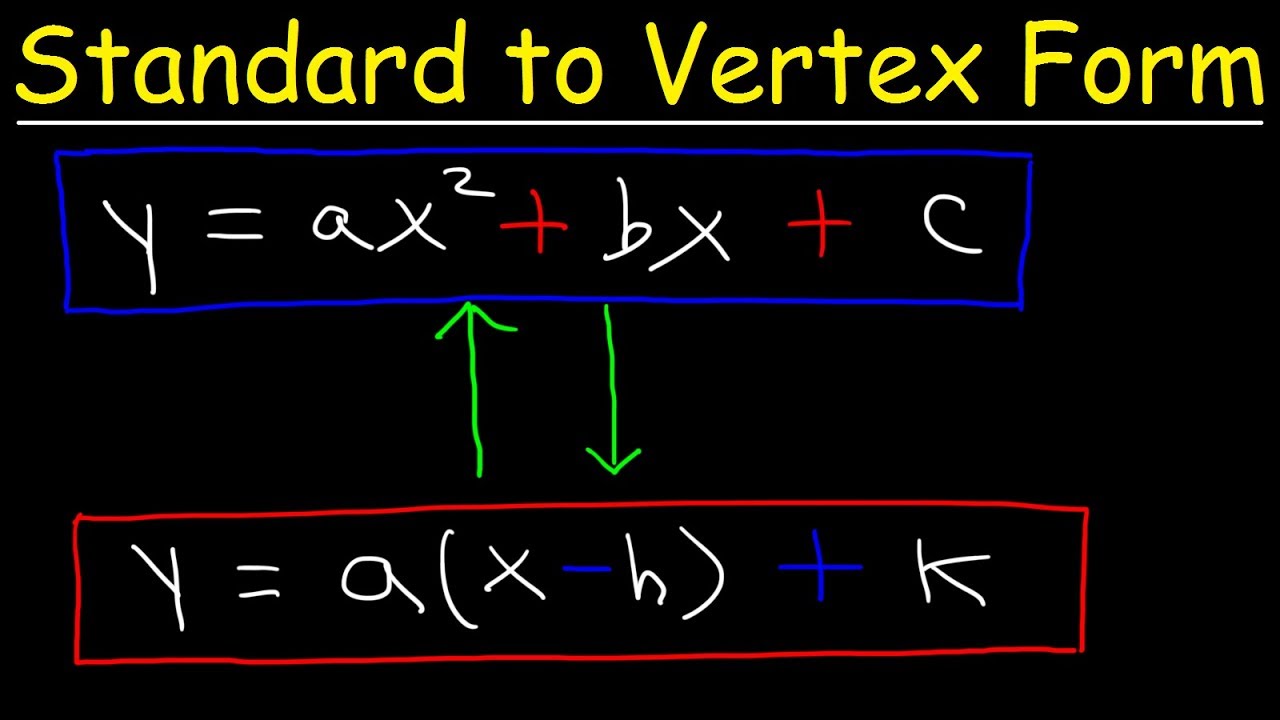
Standard Form to Vertex Form - Quadratic Equations
Standard Form to Vertex Form - Quadratic Equations
Related image with standard form quadratic function
Related image with standard form quadratic function
About "Standard Form Quadratic Function"
















Comments are closed.