Stat 217 One Sample Mean Part Ii Diagram Quizlet

STAT 217: One Sample Mean Part II Diagram | Quizlet
STAT 217: One Sample Mean Part II Diagram | Quizlet Start studying stat 217: one sample mean part ii. learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. A) using the given formula with 17.3 degrees of freedom, calculate the confidence interval for the difference in mean effect between caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee on heart rate.

STAT 217: Comparing Two Sample Mean Part II Diagram | Quizlet
STAT 217: Comparing Two Sample Mean Part II Diagram | Quizlet If our sample of size 25 produced a sample mean of 40, we might stop believing the claim (h 0: μ = 35) altogether. so what would be a reasonably cutoff for separating the unlikely values (that would lead us to reject h 0) from the values we deem are likely to have occured by random chance?. Students will learn a systematic approach to making inferences about population parameters based on sample data. Sample size: suppose we know and want to find the sample size n required to obtain a specified width for a confidence interval. for example, if = 25; what is the n required to have a 95% ci having width at most 10?. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like estimate, estimator, unbiased estimator and more.

STAT 217: Comparing Two Sample Means/ANOVA Diagram | Quizlet
STAT 217: Comparing Two Sample Means/ANOVA Diagram | Quizlet Sample size: suppose we know and want to find the sample size n required to obtain a specified width for a confidence interval. for example, if = 25; what is the n required to have a 95% ci having width at most 10?. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like estimate, estimator, unbiased estimator and more. Example 3 (one sample z test, two tailed):in a random sample of size 40 from a certain population, you obtained the sample mean sbp of 124 mmhg. assuming that you know the population standard deviation of sbp is 10 mmhg, test if the true population mean is equal to 120 mmhg or not. In this video, you will be able to:perform a full significance test for a mean with a formula or using your ti 84 calculator. Chapter 5 hypothesis testing a second type of statistical inf. rence is hypothesis testing. here, rather than use ei ther a point (or interval) estimate from a random sample to approximate a population parameter, hypothesis testing uses point estimate to decide which of two hypotheses (guesses. Suppose you have taken several samples of 10 units each from a population of 500 students, and calculated the mean of each sample. how might you use the data you now have to estimate a mean for the entire population?.
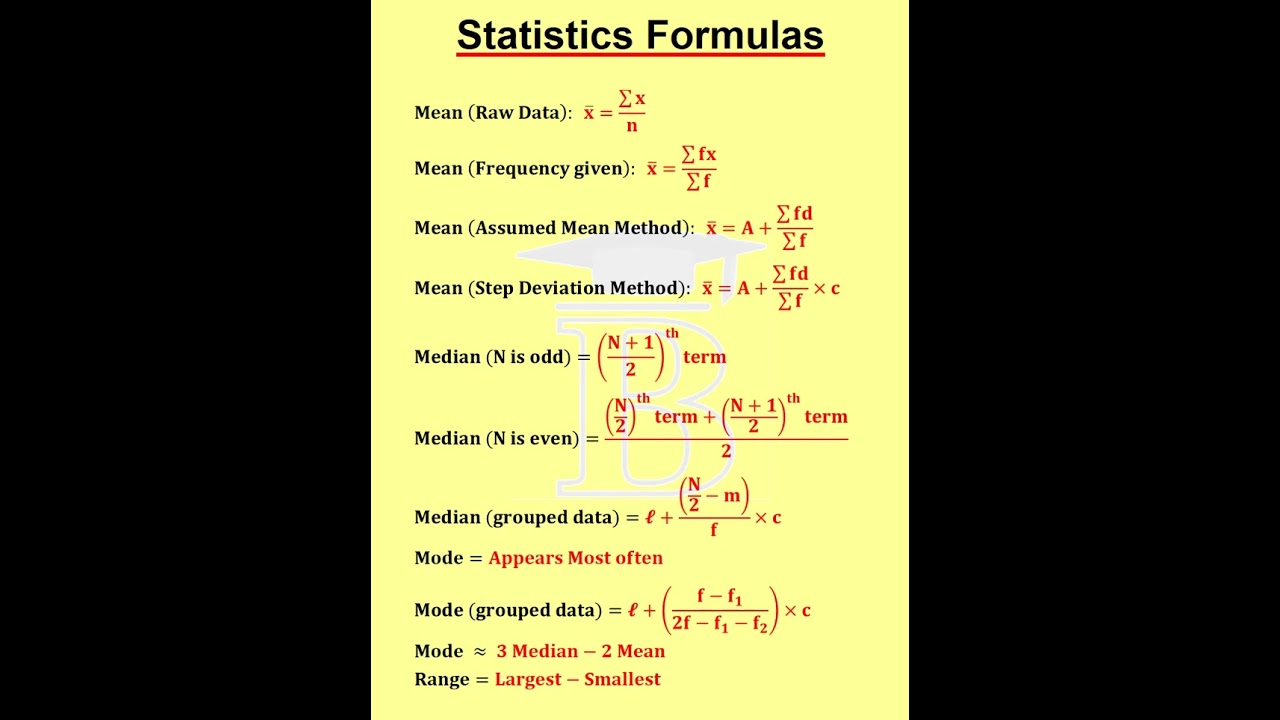
Statistics Formulas -1
Statistics Formulas -1
Related image with stat 217 one sample mean part ii diagram quizlet
Related image with stat 217 one sample mean part ii diagram quizlet
About "Stat 217 One Sample Mean Part Ii Diagram Quizlet"
















Comments are closed.