Topic 3 Kinematics In One Dimension Pdf Velocity Acceleration

Kinematics One Dimension Part 1 | PDF | Velocity | Kinematics
Kinematics One Dimension Part 1 | PDF | Velocity | Kinematics This document provides definitions and equations related to motion in one dimension. it discusses key concepts like displacement, velocity, acceleration, and how to calculate average and instantaneous values. When studying the motion of electrons around the nucleus, velocity and acceleration can be discussed to show how the electron changes speed when it encounters another electron or proton.

Topic 3: Kinematics In One Dimension | PDF | Velocity | Acceleration
Topic 3: Kinematics In One Dimension | PDF | Velocity | Acceleration Notice that acceleration relates to change in velocity exactly as velocity relates to change in displacement. velocity is a vector, so acceleration is a vector. slowing down while driving to richmond: negative acceleration. speeding up driving to skyline drive: also negative acceleration!. The sign (positive or negative) keeps track of direction (in 1 d). algebraic relations among position, velocity, and acceleration come from calculus. the same relations can be seen from graphs of position, velocity, and acceleration as functions of time. In order to fill out the information above, we should have just derived (or realized) three new kinematics formulas – a new formula for average velocity, and formulas for final velocity an acceleration. Kinematics: describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion. for now, will consider motion in one dimension along a straight line.

Chapter 2 Kinematics In One Dimension | PDF | Kinematics | Velocity
Chapter 2 Kinematics In One Dimension | PDF | Kinematics | Velocity In order to fill out the information above, we should have just derived (or realized) three new kinematics formulas – a new formula for average velocity, and formulas for final velocity an acceleration. Kinematics: describes motion while ignoring the external agents that might have caused or modified the motion. for now, will consider motion in one dimension along a straight line. This document provides an outline for a lecture on kinematics in one dimension. it covers the topics of distance and displacement, speed and velocity, and acceleration. Use free body force diagrams, algebraic expressions, and newton’s laws of motion to predict changes to velocity and acceleration for an object moving in one dimension in various situations. • relate position, velocity, and acceleration in examples of motion along one dimension. • solve numeric problems involving constant velocity and constant acceleration. average velocity is the ratio of how far an object moves to the time elapsed. Each object undergoes one stage of one dimensional motion. we are given the acceleration of the car, the velocity of the bus, and infer that the position of the car and the bus are equal when the bus just passes the car.

Kinematics | PDF | Acceleration | Velocity
Kinematics | PDF | Acceleration | Velocity This document provides an outline for a lecture on kinematics in one dimension. it covers the topics of distance and displacement, speed and velocity, and acceleration. Use free body force diagrams, algebraic expressions, and newton’s laws of motion to predict changes to velocity and acceleration for an object moving in one dimension in various situations. • relate position, velocity, and acceleration in examples of motion along one dimension. • solve numeric problems involving constant velocity and constant acceleration. average velocity is the ratio of how far an object moves to the time elapsed. Each object undergoes one stage of one dimensional motion. we are given the acceleration of the car, the velocity of the bus, and infer that the position of the car and the bus are equal when the bus just passes the car.
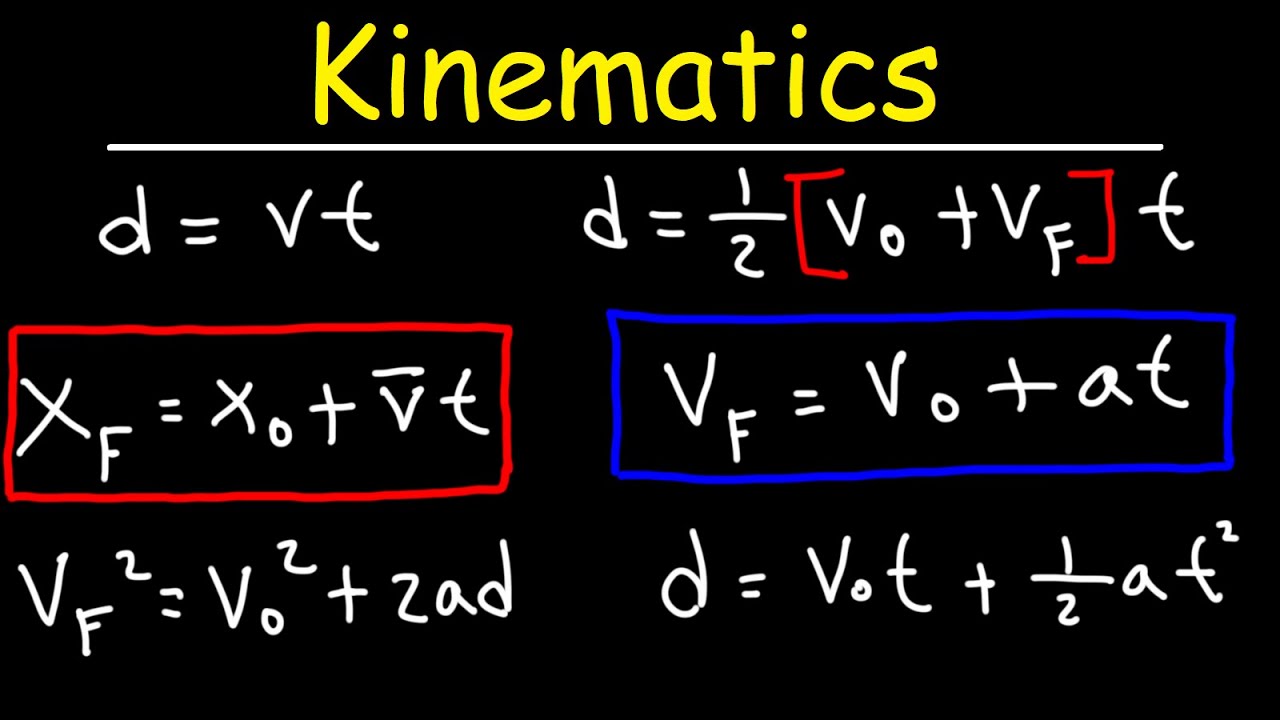
Kinematics In One Dimension - Physics
Kinematics In One Dimension - Physics
Related image with topic 3 kinematics in one dimension pdf velocity acceleration
Related image with topic 3 kinematics in one dimension pdf velocity acceleration
About "Topic 3 Kinematics In One Dimension Pdf Velocity Acceleration"
















Comments are closed.